Malaria: past, present, and future
- PMID: 40523953
- PMCID: PMC12170910
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-025-02246-3
Malaria: past, present, and future
Abstract
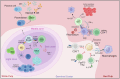
Malaria, caused by Plasmodium parasites and transmitted by Anopheles mosquitoes, greatly impacts public health and socioeconomic development, particularly in sub-Saharan African countries. Despite advances in malaria treatment and prevention, the number of clinical cases and deaths have increased in recent years. The complex life cycle and genetic diversity of Plasmodium parasites pose significant challenges in drug and vaccine development, particularly due to the emerging partial resistance of parasites to artemisinin. With the availability and application of state-of-the-art biotechnology in recent years, knowledge in terms of parasite biology, pathogenicity, host-parasite interactions and pathogenesis has advanced tremendously. This review highlights the most recent research progress and understanding in Plasmodium biology, with a primary focus on P. falciparum and associated pathogenesis. The therapeutic targets and progress in the clinical application of anti-malaria drugs have also been summarized. The FDA-approved regimens like Artemether-Lumefantrine, Atovaquone-Proguanil, and Primaquine are discussed, and their benefits and limitations are highlighted, especially in terms of drug resistance. Perspectives in the development of novel vaccines and new drugs, such as Sevuparin, Imatinib, and Cipargamin, and combination therapies with promise in overcoming resistance has been proposed. Overall, this review provides a detailed summary of the latest progress in malaria research and emphasizes the need for continuous monitoring and innovation in malaria treatment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

