Prognostic value of LncRNA SH3BP5-AS1 in non-small cell lung cancer and its regulatory effect on tumor progression
- PMID: 40523970
- PMCID: PMC12170978
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02906-4
Prognostic value of LncRNA SH3BP5-AS1 in non-small cell lung cancer and its regulatory effect on tumor progression
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the prognostic significance of SH3BP5-AS1 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, and also to uncover its function in the progression of NSCLC.
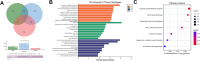
Methods: 100 NSCLC patients were recruited in this study. SH3BP5-AS1 was measured by RT-qPCR. The prognostic significance of SH3BP5-AS1 in NSCLC progression was appraised utilizing the Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression test. CCK-8 was used to detect the proliferative viability of NSCLC cells. The migratory and invasive capabilities of NSCLC cells were evaluated by Transwell assay. The interplay between SH3BP5-AS1 and miR-424-5p was verified by luciferase reporter assay and ENCORI database. The potential target genes of miR-424-5p were inspected by means of bioinformatics analysis.
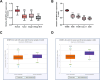
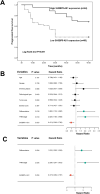
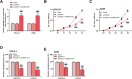
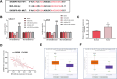
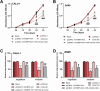
Results: A reduced SH3BP5-AS1 was manifested in tissues of NSCLC patients and tumor cells. Compared with patients showing SH3BP5-AS1 low-expression, those with SH3BP5-AS1 high-expression possessed a more favorable progression-free survival time. SH3BP5-AS1 might function as an autonomous prognostic biomarker for NSCLC. Upregulation of SH3BP5-AS1 suppressed the proliferation, migration and invasion of NSCLC cells. MiR-424-5p was a downstream target miRNA of SH3BP5-AS1, and luciferase reporter assays verified that SH3BP5-AS1 and miR-424-5p interact. In NSCLC patient tissues, miR-424-5p was upregulated and it exhibited an inverse correlation with SH3BP5-AS1. Elevation of miR-424-5p neutralized the inhibitory effect of SH3BP5-AS1 overexpression on the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of NSCLC cells.
Conclusion: SH3BP5-AS1 is involved in NSCLC development by targeting its downstream target miRNA miR-424-5p, and it is a latent prognostic indicator for NSCLC.
Keywords: Biomarker; LncRNA SH3BP5-AS1; MiR-424-5p; Non-small cell lung cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Basumallik N, Agarwal M. Small cell lung cancer. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Manuj Agarwal declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. 2024.
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A, Cancer statistics. 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
