Implications of the glymphatic system in the diagnostic and surgical workup of normal pressure hydrocephalus
- PMID: 40524080
- PMCID: PMC12394288
- DOI: 10.1007/s10072-025-08308-2
Implications of the glymphatic system in the diagnostic and surgical workup of normal pressure hydrocephalus
Abstract
Background: Magnetic Resonance (MRI) Diffusion Tensor Imaging Analysis ALong the Perivascular Space (DTI-ALPS) is a promising technique that assesses the glymphatic system (GS) function in many neurodegenerative diseases. This study aims at evaluating the role of DTI-ALPS in the diagnostic and therapeutic management of normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH).
Methods: Twenty-one NPH patients underwent 3 Tesla MRI DTI-ALPS before and after lumbar tap test (TT). Depending on the response to TT, patients were divided into a responsive cohort (15 responders, R) and non-responsive cohort (6 non-responders, NR). R patients underwent ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS) surgery, with clinical assessment upon discharge and at a 3-month follow-up (FU) visit; nine patients repeated DTI-ALPS MRI at FU. Besides, 8 matched healthy controls (HC) underwent the same MRI protocol.
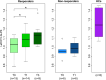
Results: The pre-TT ALPS-index in NPH patients (R: 1.003 ± 0.108, NR: 0.960 ± 0.079) was significantly lower compared to the HC (1.263 ± 0.161, p < 0.01). The pre-TT ALPS-index in R patients was higher than in NR patients, though not significantly (p = 0.39). Compared to the pre-TT values, the ALPS-index of the R group increased both post TT (1.069 ± 0.122, p = 0.0499) and post VPS (1.120 ± 0.117, p = 0.041), in accordance to the clinical outcome.
Conclusions: DTI-ALPS, reflecting the GS function, resulted significantly lower in NPH patients than in healthy controls. Secondly, clinical improvement was associated with DTI-ALPS increase both after a positive response to TT and at long term follow-up following VPS surgery. Therefore, DTI-ALPS index could be a promising, rapid and non-invasive radiological biomarker for the pre-surgical evaluation and prognosis of NPH patients.
Keywords: ALPS-index; DTI-ALPS MRI; Glymphatic System; Normal pressure hydrocephalus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical Statement: The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Local Ethics Committee (blinded for review). Informed Consent: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Conflicts of Interest: All the authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest. Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta (protocol code GlinfaNPH_2021, nr. 83/2021; date of approval: Aptil 14th, 2021).
Figures

References
-
- Adams RD, Fisher CM, Hakim S, Ojemann RG, Sweet WH (1965) Symptomatic occult hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal-fluid pressure. Va Med Mon (1918) 97(11):693–695. 10.1056/NEJM196507152730301
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

