One gene, many phenotypes: the role of KIF5A in neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental diseases
- PMID: 40524150
- PMCID: PMC12172243
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-025-02277-x
One gene, many phenotypes: the role of KIF5A in neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental diseases
Abstract
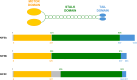
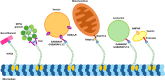
Kinesin family member 5 A (KIF5A) is a neuron-specific molecular motor involved in anterograde transport. KIF5A mediates a wide range of trafficking processes that are only partially shared with the other members of the KIF5 family. Since 2002, several disease-causing mutations have been found in the KIF5A gene and a link between the specific domain in the encoded protein affected by mutations and the associated phenotype has become evident. Point mutations targeting KIF5A motor and stalk domains, that are expected to impair KIF5A motility, mainly associate with spastic paraplegia type 10 (SPG10) and axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease. Oppositely, translational frameshifts causing the elongation of KIF5A tail enhance KIF5A migration towards cell periphery, induce kinesin aggregation, and are linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or neonatal intractable myoclonus (NEIMY). This review correlates KIF5A structure and roles in neuronal trafficking with its involvement in the above-mentioned neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental conditions.
Supplementary Information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12964-025-02277-x.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; Hereditary spastic paraplegia; KIF5A; Neonatal intractable myoclonus.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- PRIN- Progetti di ricerca di interesse nazionale - bando 2022, PNRR finanziato dall'Unione europea- Next Generation EU, componente M4C2, investimento 1.1 n. P20225R4Y5/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- PRIN-Progetti di ricerca di interesse nazionale n. 2022EFLFL8/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- 23236/AFM-Téléthon
- 739510/European Network for Rare Neurological Disorders
- piano di sviluppo della ricerca (PSR) UNIMI/Università degli Studi di Milano
- R21 AR080407/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- Travelling Fellowship n. JCSTF2205742/Company of Biologists
- R21AR080407/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RF-2018-12367768/Ministero della Salute
- . 2021-1544/Fondazione Cariplo
- Scientific Exchange Grant n. 9643/European Molecular Biology Organization
- 2025 grant/CureHSPB8,USA
- PRIN-Progetti di ricerca di interesse nazionale n. 2020PBS5MJ/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- CP 20/2018 (Care4NeuroRare)/Fondazione Regionale per la Ricerca Biomedica
- 2020 grant/Kennedy's Disease Association
- 2018 grant/Kennedy's Disease Association
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

