Hamayou () protein hydrolysate ameliorates depression by regulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
- PMID: 40524289
- PMCID: PMC12134328
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.03.007
Hamayou () protein hydrolysate ameliorates depression by regulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway
Abstract
Objective: To clarify the effect of Hamayou (Oviductus Ranae) protein hydrolysate (ORPH) on depression and its exact underlying mechanism from a new perspective.
Methods: We used the Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress (CUMS) method to prepare a mouse model of depression and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to prepare a model of BV2 cellular inflammation to investigate the antidepressant effect and mechanism of action of ORPH. Behavioral changes in mice and cerebral blood flow were detected by behavioral experiments and scatter imaging. Levels of corticosterone (CORT), proinflammatory cytokines and neurotransmitter were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Furthermore, hematoxylin-eosin staining, Tunel staining were used to evaluate the effect of ORPH. The distribution and expression of ionized calcium bindingadaptor molecule-1 (Iba-1) in mouse hippocampal tissue and BV2 cells were detected by immunofluorescence. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway related protein expression was detected by Western blot.
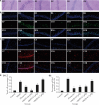
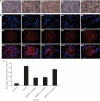
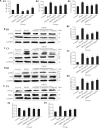
Results: ORPH improved depression-like behavior, ameliorated brain tissue damage and apoptosis, and inhibited microglia activation in brain tissue in mice. In addition, ORPH reduced expression of B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2)-associated X (Bax), cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 3 (Caspase3), cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 9 (Caspase9), nuclear factor- kappa B (NF-κB), phosphorylation-p38 (p-p38), phosphorylation-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK) proteins, and increased expression of Bcl-2, inhibitory kappa B alpha (IκB-α), phosphorylation-extracellular regulated protein kinases 1/2 (p-ERK1/2) proteins. On the other hand, there were fewer Iba-1-positive cells, lower expression of NF-κB, p-p38, p-JNK and p-ERK1/2 proteins, and higher expression of IκB-α proteins in BV2 cells in the ORPH group. In addition, ORPH increased 5-hydroxytryptamine, norepinephrine levels and decreased CORT, interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin -6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels.
Conclusion: ORPH was able to improve depression-like behaviors and that it took effects by promoting cerebral blood flow, inhibition of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis overactivation, improving the structural damage of hippocampal tissues, and inhibiting the inflammatory response. ORPH can reduced neuronal damage and inhibiting apoptosis by promoting the MAPK pathway.
Keywords: Hamayou (); apoptosis; depression; inflammation; mitogen-activated protein kinases; protein hydrolysates.
Figures

References
-
- Marwaha S, Palmer E, Suppes T, Cons E, Young AH, Upthegrove R. Novel and emerging treatments for major depression. Lancet 2023; 10371: 141-53. - PubMed
-
- Delgado P. Depression: the case for a monoamine deficiency. J Clin Psychiatry 2000; 61: 7-11. - PubMed
-
- Parker K, Schatzberg A, Lyons D. Neuroendocrine aspects of hypercortisolism in major depression. Horm Behav 2003; 43: 60-6. - PubMed
-
- Majidi J, Kosari-Nasab M, Salari A. Developmental minocycline treatment reverses the effects of neonatal immune activation on anxiety- and depression-like behaviors, hippocampal inflammation, and HPA axis activity in adult mice. Brain Res Bull 2016; 120: 1-13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
