Intervention and mechanism of Xiaoyin Anshen Yin in treatment of psoriasis combined with sleep disorders
- PMID: 40524294
- PMCID: PMC12134322
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.03.004
Intervention and mechanism of Xiaoyin Anshen Yin in treatment of psoriasis combined with sleep disorders
Abstract
Objective: To explore the therapeutic mechanisms of Xiaoyin Anshen Yin (, XYAS) in treating psoriasis associated with sleep focusing on melatonin and the regulation of the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) pathway.
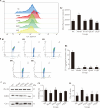
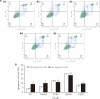
Methods: Forty Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups, and administered distilled water, XYAS and its two different disassembly prescriptions by gavage respectively. Four types of drug-containing serums corresponding to the four groups were then prepared. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α stimulated HaCaT was used to establish a psoriasis cell model, and the serums and the retinoid related orphan receptor alpha (RORα) inverse agonist were used respectively to intervene in the model. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect the levels of interleukin (IL)-6 and melatonin in each group; flow cytometry was used to detect the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), mitochondrial membrane potential, and apoptosis; Western blot was used to evaluate the levels of superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), cytochrome-c (Cyt-c), inhibitor of kappa-B alpha (IκBα), p65 and phosphorylated p65.
Results: XYAS and its disassembly prescriptions inhibited the secretion of inflammatory factors such as IL-6, reduced the ROS content and Cyt-c expression, increased the mitochondrial membrane potential and SOD2 content, promoted the apoptosis in HaCaT cells and inhibited the activation of the NF-κB pathway. XYAS was also found increase the melatonin content. The above effects are beneficial in the treatment of psoriasis combined with sleep disorders. Meanwhile, XYAS no longer had a significant ameliorative effect after applying the RORα inverse agonist, suggesting that the therapeutic effect of XYAS is related to RORα.
Conclusions: The results of this study confirm that XYAS can be utilized for the treatment of psoriasis combined with sleep disorders via inhibiting the NF-κB pathway, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and pro-apoptotic, which is in part related to the regulatory role of melatonin and its receptor RORα.
Keywords: NF-kappa B; melatonin; nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group F, member 1; psoriasis; sleep disorder.
Figures
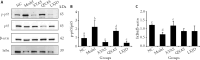

References
-
- Griffiths CEM, Armstrong AW, Gudjonsson JE, Barker JNWN. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021; 397: 1301-15. - PubMed
-
- Menter A, Strober BE, Kaplan DH, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol 2019; 80: 1029-72. - PubMed
-
- Baranwal N, Yu PK, Siegel NS. Sleep physiology, pathophysiology, and sleep hygiene. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2023; 77: 59-69. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
