Rotating-pulling-poking manipulation in gait analysis for lateral ankle sprain treatment
- PMID: 40524306
- PMCID: PMC12134312
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.03.019
Rotating-pulling-poking manipulation in gait analysis for lateral ankle sprain treatment
Abstract
Objective: To compare the changes in gait parameters before and after the treatment of lateral ankle sprain using the rotating-pulling-poking manipulation, and explore the potential bio-mechanical mechanism of this manipulation.
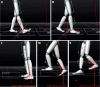
Methods: Forty patients with lateral ankle sprains were randomly divided into two groups in a 1:1 ratio using a random number table. The experimental group were treated by rotating-pulling-poking manipulation and elastic bandage external fixation, while the control group were treated by ice compress and elastic bandage external fixation. The treatment courses of the two groups were both 2 weeks. We used a three-dimensional motion capture system for kinematic measurements and a Bertec gait analysis force measurement system for mechanical measurements, and compared the changes in gait parameters between the two groups of patients before and after treatment.
Results: Intragroup comparison showed that the support time, swing time, peak of back extension, peak of plantar flexion, peak of toe pedal force, and peak of heel landing force of the affected feet in the experimental group were significantly improved compared to those before treatment (P < 0.05). The swing time of the affected feet in the control group was significantly improved compared to that before treatment (P < 0.05). The inter group comparison showed that the gait speed, stride length, peak of back extension, peak of plantar flexion, peak of toe pedal force, and peak of heel landing force of the affected feet in the experimental group were significantly better than those in the control group (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: The rotating-pulling-poking manipulation can effectively improve the patient's gait and range of motion of the affected ankle joint, and enhance the negative gravity in the vertical direction of the affected foot, and the braking and driving forces in the front and back directions. This may be the potential biomechanical mechanism of the rotating-pulling-poking manipulation for treating lateral ankle sprain.
Keywords: gait analysis; lateral ankle sprain; rotating-pulling-poking manipulation.
Figures

References
-
- Martin RL, Davenport TE, Fraser JJ, et al. Ankle stability and movement coordination impairments: lateral ankle ligament sprains revision 2021. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2021; 51: Cpg1-80. - PubMed
-
- Miklovic TM, Donovan L, Protzuk OA, Kang MS, Feger MA. Acute lateral ankle sprain to chronic ankle instability: a pathway of dysfunction. Phys Sportsmed 2018; 46: 116-22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- ZYYCXTD-C-202003/National Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Innovation Team Project: Traditional Chinese Medicine Innovation Team for Prevention and Treatment of Bone and Joint Degenerative Diseases
- 81473694/National Natural Science Foundation of China: the study on the Quantification and Mechanism of the rotating-pulling-poking manipulation in the Treatment of Lateral Ankle Sprain
- CI2021A02015/China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences Science and Technology Innovation Project: Establishment and Promotion of a Simulation Operation Evaluation System for Rotating-pulling-poking Manipulation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
