Proton-pump inhibitors increase C. difficile infection risk by altering pH rather than by affecting the gut microbiome based on a bioreactor model
- PMID: 40524314
- PMCID: PMC12184164
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2519697
Proton-pump inhibitors increase C. difficile infection risk by altering pH rather than by affecting the gut microbiome based on a bioreactor model
Abstract
Clostridioides difficile infections often occur after antibiotic use, but they have also been linked to proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy. The underlying mechanism - whether infection risk is due to a direct effect of PPIs on the gut microbiome or changes in gastrointestinal pH - has remained unclear. To disentangle both possibilities, we studied the impact of the proton-pump inhibitor omeprazole and pH changes on key members of the human gut microbiome and stool-derived microbial communities from different donors in vitro. We then developed a custom multiple-bioreactor system to grow a model human microbiome community and a stool-derived community in chemostat mode and tested the effects of omeprazole exposure, pH changes, and their combination on C. difficile growth within these communities. Our findings show that changes in pH significantly affect the gut microbial community's biomass and the abundances of different bacterial taxa, leading to increased C. difficile growth within the community. However, omeprazole treatment alone did not result in such effects. These findings imply that the higher risk of C. difficile infection following proton-pump inhibitor therapy is probably because of alterations in gastrointestinal pH rather than a direct interaction between the drug and the microbiome. This understanding offers a new perspective on infection risks in proton-pump inhibitor therapy.
Keywords: Proton-pump inhibitor; bioreactor; clostridioides difficile infection; colonization resistance; gut microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
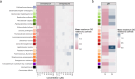


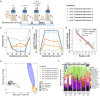
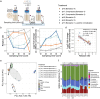
References
-
- Guh AY, Adkins SH, Li Q, Bulens SN, Farley MM, Smith Z, Holzbauer SM, Whitten T, Phipps EC, Hancock EB, et al. Risk factors for community-associated Clostridium difficile infection in adults: a case-control study. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017;4(4):ofx171. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofx171. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Furuya-Kanamori L, Stone JC, Clark J, McKenzie SJ, Yakob L, Paterson DL, Riley TV, Doi SAR, Clements AC. Comorbidities, exposure to medications, and the risk of community-acquired Clostridium difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2015;36(2):132–21. doi: 10.1017/ice.2014.39. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
