A Japanese Case of Lenz-Majewski Syndrome With a Novel PTDSS1 Variant
- PMID: 40524567
- PMCID: PMC12171241
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.70112
A Japanese Case of Lenz-Majewski Syndrome With a Novel PTDSS1 Variant
Abstract
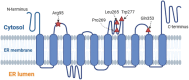
Background: Lenz-Majewski syndrome (LMS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by osteosclerosis, intellectual disability, characteristic facies, and distinct craniofacial, dental, cutaneous, and distal-limb anomalies. Mutations in the PTDSS1 gene, which encodes one of the phosphatidylserines (PS) synthase enzymes, PSS1, have been identified as causative in LMS patients. These mutations make PSS1 insensitive to feedback inhibition by PS levels.
Methods: Whole genome sequence (WGS) was performed on a patient with congenital cutis laxa and her parents. PS synthase activity was analyzed in PTDSS1 mutant cDNA clones to evaluate functional alterations.
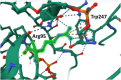
Results: A 5-year-old girl presented with congenital skin wrinkles and was initially diagnosed with congenital cutis laxa. She had bilateral inner ear hypoplasia, bilateral low-frequency hearing loss, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and mild intellectual disability. Physical examination revealed protruding ears, frontal bossing, and dental malalignment. A de novo heterozygous missense variant in the PTDSS1 gene, c.284G>A (p. Arg95Gln) was identified by WGS. Functional analysis indicated increased PS synthase activity, supporting the pathogenicity of this variant.
Conclusions: The patient's cutis laxa and facial features were consistent with LMS, though radiographic findings did not reveal the characteristic sclerosing bone dysplasia reported in previous cases. This observation suggests that LMS may have a broader phenotypic spectrum than previously recognized.
Keywords: Lenz‐Majewski syndrome; PTDSS1 gene; congenital cutis laxa; phenotypic spectrum.
© 2025 The Author(s). Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have received financial support from Astellas Pharma Inc. and declare this as a competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Afifi, H. H. , Abdel‐Hamid M. S., Mehrez M. I., El‐Kamah G., and Abdel‐Salam G. M. H.. 2019. “Lenz–Majewski Syndrome in a Patient From Egypt.” American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A 179, no. 10: 2039–2042. - PubMed
-
- Bevers, E. M. , and Williamson P. L.. 2016. “Getting to the Outer Leaflet: Physiology of Phosphatidyl‐Serine Exposure at the Plasma Membrane.” Physiological Reviews [Internet] 96: 605–645. www.prv.org. - PubMed
-
- Braham, R. L. 1969. “Multiple Congenital Abnormalities With Diaphyseal Dysplasia (Camurati‐Engelmann's Syndrome). Report of a Case.” Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, and Oral Pathology 27, no. 1: 20–26. - PubMed
-
- Dateki, S. , Kondoh T., Nishimura G., et al. 2007. “A Japanese Patient With a Mild Lenz‐Majewski Syndrome.” Journal of Human Genetics 52, no. 8: 686–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

