Identification of pediatric MASLD using insulin resistance indices
- PMID: 40524700
- PMCID: PMC12167474
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2025.101419
Identification of pediatric MASLD using insulin resistance indices
Abstract
Background & aims: We investigated the triglyceride-to-high density lipoprotein (HDL) ratio (TG/HDL), triglyceride-glucose index (TyG), single-point insulin sensitivity estimator (SPISE), and metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) as potential predictors of pediatric metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) by addressing the limited research on insulin-resistance markers in this population.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included data from 1,150 and 260 youths from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) and a real-world clinic, respectively. Hepatic steatosis was assessed using transient elastography and abdominal sonography. Logistic regression analysis was performed using MASLD as the dependent variable. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to evaluate predictability.
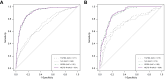
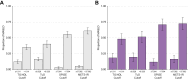
Results: The MASLD group had higher TG/HDL, TyG, METS-IR, and obesity proportions but lower SPISE than the normal group in both NHANES and real-world data. All markers were significantly related to MASLD in logistic regression analyses, even after adjusting for age and sex, in both the NHANES and real-world clinic data (all p <0.001). The areas under the ROC curves (AUCs) for SPISE and METS-IR were 0.91 and 0.91 in the total group, 0.92 and 0.92 in the male group, and 0.90 and 0.89 in the female group, respectively-all higher than those for TG/HDL and TyG in the NHANES dataset (all p <0.001). In the real-world clinical data, the AUCs of SPISE and METS-IR were significantly higher than those of TG/HDL and TyG in the total and male groups (all p <0.001). In the female group, the AUC for SPISE was significantly higher than that for TG/HDL or TyG.
Conclusions: METS-IR and SPISE are effective, non-invasive markers for predicting pediatric MASLD, which offer valuable tools for early detection and improved clinical management.
Impact and implications: The increasing prevalence of pediatric metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its strong association with cardiometabolic risk factors underscore the need for effective early detection tools. Our study demonstrates that single-point insulin sensitivity estimator (SPISE) and metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) are superior, non-invasive markers for predicting MASLD in children and adolescents, with validated cut-off values applicable to both population-based and real-world clinical settings. These findings are particularly relevant for clinicians and healthcare policymakers, as they provide practical, easily accessible screening tools derived from routine laboratory tests, aiding in the early identification and risk stratification of pediatric MASLD. However, given the study's retrospective design and variations in diagnostic methods across datasets, further validation in larger, diverse cohorts is warranted to refine age-specific cut-off values and optimize screening approaches.
Keywords: Adolescent; Biomarkers; Child; Insulin resistance; Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest that pertain to this work. Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of SPISE and METS-IR and Other Markers to Predict Insulin Resistance and Elevated Liver Transaminases in Children and Adolescents.Diabetes Metab J. 2025 Mar;49(2):264-274. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0302. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Diabetes Metab J. 2025. PMID: 39532082 Free PMC article.
-
A Single-Point Insulin Sensitivity Estimator (SPISE) of 5.4 is a good predictor of both metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in adolescents with obesity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 8;14:1078949. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1078949. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36843603 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a nomogram based on METS-IR and SPISE index for predicting mild cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 Jul 22. doi: 10.1007/s40618-025-02629-x. Online ahead of print. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 40694298
-
Comparison of the triglyceride glucose (TyG) index, triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio, and metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) associated with periodontitis in Korean adults.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022 Sep 12;13:20406223221122671. doi: 10.1177/20406223221122671. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022. PMID: 36120508 Free PMC article.
-
Screening accuracy of Single-Point Insulin Sensitivity Estimator (SPISE) for metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 Jun 6;25(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01957-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 40481439 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of estimated glucose disposal rate with risk of future metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and other chronic liver diseases: a prospective cohort study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 2;12:1589245. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1589245. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40672815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rinella M.E., Lazarus J.V., Ratziu V., et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J Hepatol. 2023;79:1542–1556. - PubMed
-
- Song K., Park G., Lee H.S., et al. Trends in prediabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease associated with abdominal obesity among Korean children and adolescents: based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2009 and 2018. Biomedicines. 2022;10:584. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Miao L., Targher G., Byrne C.D., et al. Current status and future trends of the global burden of MASLD. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2024;35:697–707. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

