Radiation-Based Multi-Modal Therapy Combining with Immunotherapy to Develop a Vaccine-Like Effective Treatment for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 40524764
- PMCID: PMC12169013
- DOI: 10.2147/BCTT.S518625
Radiation-Based Multi-Modal Therapy Combining with Immunotherapy to Develop a Vaccine-Like Effective Treatment for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive malignancy with high metastasis and recurrence rates. Current treatments like chemotherapy and immunotherapy face challenges due to chemotherapy side effects, limited immunotherapy applicability, and TNBC's immunosuppressive microenvironment.
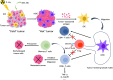
Purpose: To achieve a more effective treatment for TNBC, a novel therapeutic strategy has been developed, which uses X-ray excited photodynamic therapy (X-PDT) to activate the tumor immune microenvironment following with the immunotherapy of Anti-CTLA4.
Methods: Base on the 4T1 tumor mouse model, this study initially investigated the regulatory effects of X-PDT on the tumor immune microenvironment. Subsequently, the therapeutic efficacy of combining X-PDT with Anti-CTLA4 was evaluated for its inhibitory effects on primary, metastatic, and recurrent tumors. The underlying mechanisms were further elucidated through comprehensive techniques including flow cytometry, ELISA, and immunofluorescence assays.
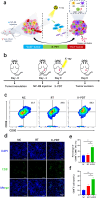
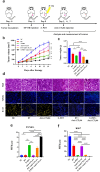
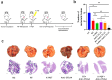
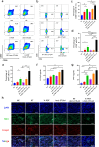
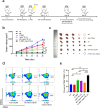
Results: The synergistic strategy can effectively ablate the primary tumor while inhibiting metastasis and preventing recurrence like a vaccine. It enhances intratumoural dendritic cells (DCs) maturation (from 25.7% to 58.3%, P < 0.05) and immune T cell infiltration activating a strong anti-tumor immune response. The anti-tumor efficacy of synergistic therapy is enhanced by 2.5 times comparing with immunotherapy alone, while the tumor metastasis has been inhibited significantly. The maturation level of mature dendritic cells was increased from 26.7% to 86.3% (P < 0.01). The intratumoural CD8+/CD4+ T cells were increased from 0.51% and 1.54% to 15.4% and 23.1% (P < 0.0001), respectively. The synergistic therapy exerts a powerful vaccine-like long-term immune memory function to prevent tumor recurrence with the elevated level of effector memory T (Tem) cells (from 12.8% to 33.3%, P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Based on the 4T1 mouse model, developed an effective vaccine-like therapeutic strategy combining X-PDT with Anti-CTLA4, which can effectively ablate tumors, inhibit metastasis, and prevent tumor recurrence. This work may provide a novel effective therapeutic modality for the clinical treatment of TNBC.
Keywords: X-ray excited photodynamic therapy; cancer vaccine; combination therapies; immunotherapy; nanodrugs.
© 2025 Dai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An immunomodulatory photosensitizer-mediated photodynamic therapy synergizes with PD-L1 blockade against metastatic triple-negative breast cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 17;16:1651165. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1651165. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40746718 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular feature-based classification of retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a prospective cohort study.Elife. 2025 May 23;14:RP100887. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100887. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40407808 Free PMC article.
-
High tumor expression of CTLA4 identifies lymph node-negative basal-like breast cancer patients with excellent prognosis.Commun Med (Lond). 2025 Jun 16;5(1):234. doi: 10.1038/s43856-025-00865-z. Commun Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40523912 Free PMC article.
-
Why combine and why neoadjuvant? Tumor immunological perspectives on chemoimmunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2025 Jul;32(4):676-688. doi: 10.1007/s12282-025-01707-5. Epub 2025 May 6. Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40327275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

