[18F]FDG-PET/CT in DLBCL-patients treated with CAR-T cell therapy: potential for defining patient prognosis
- PMID: 40524784
- PMCID: PMC12169787
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2025.100663
[18F]FDG-PET/CT in DLBCL-patients treated with CAR-T cell therapy: potential for defining patient prognosis
Abstract
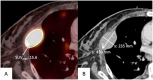
Objectives: The aim of this study is to evaluate the potential of [18F]FDG-PET/CT in terms of prognostic value and treatment monitoring in relapsed / refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)-patients treated with chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy.
Material & methods: Forty-eight [18F]FDG-PET/CT scans, acquired at pre-defined time points (t0 - t2) of 18 DLBCL-patients (mean age: 60 ± 12 years) treated with CAR-T cell therapy were retrospectively enrolled. Median time of follow-up was ten months (IQR 6-16) following CAR-T cell infusion. SUVmax, sum of the product of diameters (SPD), Deauville score (DS) and Lugano classification (LC) were evaluated. Clinical parameters (age, sex) were obtained. Survival time analyses for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated, the latter by using the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox regression including a hazard ratio (HR). P values below 0.05 were defined as statistically significant. 95 %-confidence intervals (CI) were calculated.
Results: Patients with a SUVmax> 9.0 at t0 (median as threshold value) had a significantly shorter PFS (p = 0.04) and OS (p < 0.01). According to LC, a progressive disease (PD) at t1 (p = 0.02) and t2 (p < 0.01) was correlated with a reduced OS. SUVmax > 9.0 at t0 (p = 0.03, HR = 7.0, CI: 1.3-40.5) and DS > 3 at t1 (p = 0.04, HR = 8.2, CI: 1.1-61.3) were associated with an increased risk of a PD.
Conclusion: SUVmax of [18F]FDG-PET/CT seems to be useful as a prognostic marker in DLBCL-patients undergoing CAR-T cell therapy. Furthermore, scores of clinical established Deauville classification and Lugano response criteria acquired at post-CAR-T [18F]FDG-PET/CT might be an indicator for early therapy failure.
Keywords: CAR-T; Diffuse large B cell lymphoma; FDG-PET/CT; Overall survival; Progression-free survival.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Schuster S.J., et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;380(1):45–56. - PubMed
-
- Schuster S.J., Investigators J. Tisagenlecleucel in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;380(16):1586. - PubMed
-
- Abramson J.S., et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396(10254):839–852. - PubMed
-
- Locke F.L., et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel as second-line therapy for large b-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022;386(7):640–654. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

