Meta-analysis study of the therapeutic impact of Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes for chronic kidney diseases
- PMID: 40524833
- PMCID: PMC12169747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102072
Meta-analysis study of the therapeutic impact of Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes for chronic kidney diseases
Abstract
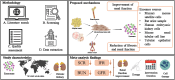
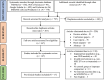
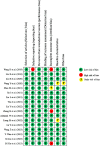
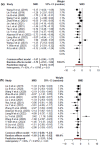
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (EXOs) represent a promising avenue for treating chronic kidney diseases (CKD), though their precise impact remains somewhat elusive. To address this gap, we conducted a systematic analysis, scouring databases and clinical trial repositories for relevant studies from 2019 to 2023. Seventeen papers were meticulously selected for their focus on mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-EXOs) and their potential in CKD treatment. Our comprehensive meta-analysis, incorporating 15 preclinical and 6 clinical studies, underscores the efficacy of MSC-EXOs in improving renal function while attenuating tubular injury, inflammation, apoptosis, collagen deposition, and renal fibrosis. Notably, post-treatment with MSC-EXOs exhibited significant associations with various CKD markers, with pooled proportions indicating a considerable impact on blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (SCR) levels. Subgroup analyses based on animal models further elucidated heterogeneity within the studies. In conclusion, MSC-EXOs demonstrate promise in enhancing renal function and reducing CKD risk, as evidenced by both preclinical and clinical data. Their efficacy in lowering SCR and BUN levels while enhancing filtration rate suggests MSC-EXOs as a viable and secure alternative to cell-based therapies, thereby providing valuable insights for personalized CKD treatments despite inherent limitations.
Keywords: Chronic kidney diseases; Exosome; Mesenchymal stem cells; Meta-analysis; Renal fibrosis.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective effects and possible mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells and mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles against kidney fibrosis in animal models: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 3;15:1511525. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1511525. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39830341 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-125b-5p deriving from mesenchymal stem cells promotes tubular repair by suppression of p53 in ischemic acute kidney injury.Theranostics. 2021 Mar 11;11(11):5248-5266. doi: 10.7150/thno.54550. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33859745 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 21;9:816656. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.816656. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35386912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single and combined strategies for mesenchymal stem cell exosomes alleviate liver fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical animal models.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 31;15:1432683. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1432683. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39144628 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional culture of MSCs produces exosomes with improved yield and enhanced therapeutic efficacy for cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 May 27;11(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01719-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32460853 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

