In Silico Bioprospection of Daniellia oliveri- Based Products as Quorum Sensing Modulators of Escherichia coli SdiA
- PMID: 40524946
- PMCID: PMC12170066
- DOI: 10.1155/bri/7191508
In Silico Bioprospection of Daniellia oliveri- Based Products as Quorum Sensing Modulators of Escherichia coli SdiA
Abstract
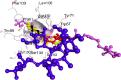
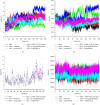
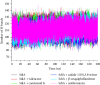
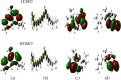
Escherichia coli is a common pathogen responsible for various gut-related infections, and it utilizes the SdiA-mediated quorum sensing (QS) system to regulate biofilm formation, other virulence factors, and pathogenicity. With rising antibiotic resistance, there is a pressing need to discover alternative QS inhibitors (QSIs) targeting SdiA. This study evaluated 239 phytochemicals from Daniellia oliveri as potential SdiA modulators using in silico techniques. Virtual screening identified four lead compounds (cadala-1(10),3,8-triene, carotenoid K, valencene, and β-sesquiphellandrene), with carotenoid K (-53.71 kcal/mol) exhibiting a higher binding free energy compared to the standard, azithromycin (-52.19 kcal/mol), following dynamics simulation. Notably, the SdiA-carotenoid K complex demonstrated enhanced thermodynamic stability with a root mean square deviation (RMSD) of 2.64 Å. All four leads, except carotenoid K, conformed to the Lipinski rule for selection of candidates that could be administered orally. Quantum chemical feature analyses using DFT/B3LYP showed that carotenoid K had the lowest HOMO-LUMO energy gap, high ionization energy, and electrophilicity index values, indicating its superior reactivity and stability. These properties suggest enhanced interactions with the SdiA active site compared to other investigated compounds. These observations highlight carotenoid K as a promising modulator of SdiA. However, further structural modification and validation through in vitro and in vivo studies are recommended.
Keywords: Daniellia oliveri; E.coli; MD simulation; SdiA; molecular docking; quorum sensing.
Copyright © 2025 Yamkela Dweba et al. Biochemistry Research International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abed A., Khudhair A., Hussein I. Effects of Misuse of Antibiotics on the Resistance of Escherichia coli Isolated From the Intestines of Broiler Chickens. International Journal of Drug Delivery Technology . 2020;10(2):190–194. doi: 10.25258/ijddt.10.2.1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

