Integrating Network Pharmacology and in vivo Validation to Explore the Mechanisms of Buyang Huanwu Decoction in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 40524966
- PMCID: PMC12169005
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S512050
Integrating Network Pharmacology and in vivo Validation to Explore the Mechanisms of Buyang Huanwu Decoction in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
Objective: Buyang Huanwu Decoction (BYHWD), a traditional Chinese herbal formula, has been widely used to manage cardiovascular disorders. However, its cardioprotective mechanisms in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MI/RI) remain unclear. This study aims to investigate its pharmacological mechanisms against MI/RI through network pharmacology and experimental validation.
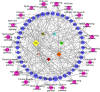
Materials and methods: Active components and targets of BYHWD were identified via Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform, Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine, BATMAN-TCM, and SymMap databases. MI/RI-related targets were retrieved from DisGeNET, GeneCard, Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, Comparative Toxicogenomics Database, and DrugBank databases. The intersecting targets were analyzed using Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, compound-target networks, and herb-target-pathway networks were constructed using Cytoscape, and molecular docking was performed via AutoDock Vina. A rat MI/RI model was used to assess infarct size, protein expression, and cytokine levels for in vivo validation.
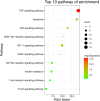
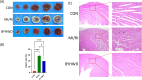
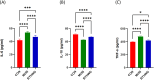
Results: 95 compounds were identified, with 75 MI/RI-related targets. PPI analyses highlighted ten hub genes, including interleukin-6 (IL6), AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (AKT1), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1), matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), interleukin-10 (IL10), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM1), nitric oxide synthase 3, albumin, and C-reactive protein. GO and KEGG analyses highlighted TNF signaling, apoptosis, and p53 signaling pathways. Carthami Flos and Radix Astragali emerged as core herbs, with quercetin, kaempferol, baicalein, stigmasterol, baicalin, and beta-sitosterol as key compounds exhibiting strong binding affinities to hub genes. In vivo, BYHWD significantly reduced myocardial infarct size, decreased inflammatory cytokines (IL6 and TNF-α), ICAM1, VCAM1, and MMP9 protein expression, and IL10 and phosphorylated AKT1 expression.
Conclusion: BYHWD alleviates MI/RI through multicomponent, multitarget, and multipathway mechanisms, primarily modulating TNF and AKT1-mediated inflammatory/apoptotic pathways. These effects collectively support its potential as a complementary treatment for ischemic heart disease.
Keywords: Buyang Huanwu decoction; myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury; network pharmacology.
© 2025 Luo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Yushan Luo, Wen Hu, Ziyue Li and Xiaoyuan Zhang contributed equally and share co-first authors for this study. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Elucidating the Mechanism of Xiaoqinglong Decoction in Chronic Urticaria Treatment: An Integrated Approach of Network Pharmacology, Bioinformatics Analysis, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025 Jul 16. doi: 10.2174/0115734099391401250701045509. Online ahead of print. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 40676786
-
Revealing the Multi-Target Mechanisms of Fespixon Cream in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing: Integrated Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Clinical RT-qPCR Validation.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jun 25;47(7):485. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070485. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40728954 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics and experimental validation reveal the mechanism of DanxiaTiaoban decoction in treating atherosclerosis.Phytomedicine. 2025 Aug 31;147:157216. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157216. Online ahead of print. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40916281
-
Study on the mechanism of Shujin Tongluo granules in treating cervical spondylosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jul 21;102(29):e34030. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034030. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37478234 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the mechanism of ShenGui capsule in treating heart failure based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Apr 5;103(14):e37512. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037512. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38579077 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

