Aortic Dissection After Self-Expanding Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
- PMID: 40525199
- PMCID: PMC12167550
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atssr.2024.10.020
Aortic Dissection After Self-Expanding Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Abstract
Aortic dissection after transcatheter aortic valve replacement is rare but can be managed with open surgical repair. Principles of repair are the same as in patients with spontaneous aortic dissection; however, all procedures include transcatheter aortic valve replacement explantation and subsequent aortic valve replacement. A high index of suspicion facilitates early recognition and effective surgical repair.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures
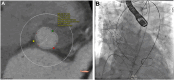
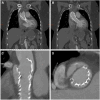
References
-
- Thomas M., Schymik G., Walther T., et al. Thirty-day results of the SAPIEN aortic Bioprosthesis European Outcome (SOURCE) registry: a European registry of transcatheter aortic valve implantation using the Edwards SAPIEN valve. Circulation. 2010;122:62–69. - PubMed
-
- Berfield K.K., Sweet M.P., McCabe J.M., et al. Endovascular repair for type A aortic dissection after transcatheter aortic valve replacement with a Medtronic CoreValve. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;100:1444–1446. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

