Plasmonic ELISA for Biomarker Detection: A Review of Mechanisms, Functionalization Strategies, and Emerging Modalities
- PMID: 40525845
- PMCID: PMC12284857
- DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.5c00738
Plasmonic ELISA for Biomarker Detection: A Review of Mechanisms, Functionalization Strategies, and Emerging Modalities
Abstract
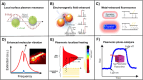
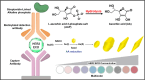
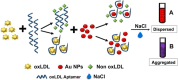
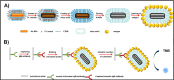
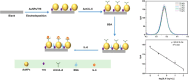
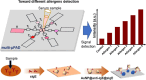
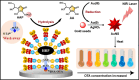
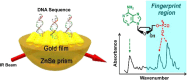
Plasmonic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) effectively integrates noble metal nanostructures with traditional immunoassays, facilitating rapid, ultrasensitive, and multiplexed biomarker detection. By leveraging localized surface plasmon resonance modulations instigated by biocatalytic reactions and analyte binding, these assays achieve signal amplification through growth, etching, and aggregation mechanisms. Such methodologies significantly enhance detection limits by factors ranging from 10- to over 1000-fold, attaining sensitivity at the subpicogram per milliliter level. Robust surface functionalization methods, including electrostatic adsorption, covalent coupling, and affinity binding, ensure stable immobilization of antibodies while preserving the activity of the nanozymes. Incorporating advanced two-dimensional nanomaterials, such as graphene derivatives and MXenes, further augments the sensitivity (up to ∼200-fold), assay stability, and potential for miniaturization. Emerging modalities, including electrochemical techniques, microfluidics, photothermal methods, surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA), surface-enhanced Raman scattering, and CRISPR-enabled ELISA, extend the analytical versatility, multiplexing capabilities, and operational speed. Clinical trials, alongside real-world studies, substantiate the efficacy of plasmonic ELISA platforms in early cancer detection, diagnostic evaluation of infectious diseases, and monitoring cardiovascular biomarkers, demonstrating performance comparable to or exceeding that of traditional methodologies. Despite significant advancements, challenges persist with regard to assay standardization, multiplex integration, and large-scale manufacturing. This review presents a comprehensive overview of recent developments, identifies critical knowledge gaps, and outlines future perspectives to expedite the clinical translation of plasmonic ELISA technologies for precision medicine and global health applications.
Keywords: biomarker detection; clinical diagnostics; multiplexed biosensing; nanoparticle surface functionalization; plasmonic ELISA.
Figures





References
-
- Aydin S., Emre E., Ugur K., Aydin M. A., Sahin İ., Cinar V., Akbulut T.. An Overview of ELISA: A Review and Update on Best Laboratory Practices for Quantifying Peptides and Proteins in Biological Fluids. J. Int. Med. Res. 2025;53(2):3000605251315913. doi: 10.1177/03000605251315913. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Z., Ma A., Miller I., Starnes R., Talkington A., Stone C. A., Phillips E. J., Choudhary S. K., Commins S. P., Lai S. K.. Development of Anti-PEG IgG/IgM/IgE ELISA Assays for Profiling Anti-PEG Immunoglobulin Response in PEG-Sensitized Individuals and Patients with Alpha-Gal Allergy. J. Controlled Release. 2024;366:342–348. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.01.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iralu, N. ; Wani, S. ; Meghanath, D. ; Saleem, S. ; Hamid, A. . Direct Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for Detection of Plant Viruses. In Detection of Plant Viruses: Advanced Techniques; Hamid, A. , Ali, G. , Shikari, A. , Saleem, S. , Wani, S. H. , Wani, S. , Eds.; Springer US: New York, NY, 2025; pp 35–41. 10.1007/978-1-0716-4390-7_9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
