The dual role of type I interferons in bacterial infections: from immune defense to pathogenesis
- PMID: 40525851
- PMCID: PMC12239577
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.01481-25
The dual role of type I interferons in bacterial infections: from immune defense to pathogenesis
Abstract
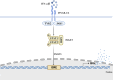
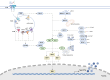
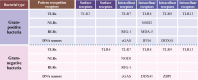
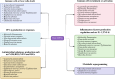
Type I interferons (IFNs) are crucial components of the human immune system, playing a key role in regulating immune activity. Existing literature has characterized their antiviral and proviral roles in viral contexts. Type I IFNs also exhibit a dual role in bacterial infections, functioning as defenders or disruptors or both based on factors including but not limited to such things as the bacterial species, infection stage, host immune status, and the route and site of infection. This review provides a summary of the signaling pathways associated with type I IFN responses and discusses the complex mechanisms of type I IFNs in bacterial infections. Because type I IFNs provide an important opportunity to develop personalized treatment strategies, which are expected to be transformed into efficient adjuvant therapy for specific infectious diseases, we also discuss the potential for targeting type I IFNs for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: bacterial infection; host immunity; type I interferon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING)-Type I Interferon Signaling: Bridging Immunity and Pain.J Integr Neurosci. 2025 Jun 23;24(6):33414. doi: 10.31083/JIN33414. J Integr Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40613364 Review.
-
The Human Papillomavirus E6 Oncoprotein Targets USP15 and TRIM25 To Suppress RIG-I-Mediated Innate Immune Signaling.J Virol. 2018 Feb 26;92(6):e01737-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01737-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29263274 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Type I interferons for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD006790. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006790.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 14;(9):CD006790. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006790.pub3. PMID: 18646167 Updated.
-
A MicroRNA Screen Identifies the Wnt Signaling Pathway as a Regulator of the Interferon Response during Flavivirus Infection.J Virol. 2017 Mar 29;91(8):e02388-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02388-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28148804 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

