Antigenic Protein Screening and Design of Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Lactococcus garvieri and Streptococcus iniae for Combating Lactococcosis and Streptococcosis in Fish
- PMID: 40526224
- PMCID: PMC12172566
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.70465
Antigenic Protein Screening and Design of Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Lactococcus garvieri and Streptococcus iniae for Combating Lactococcosis and Streptococcosis in Fish
Abstract
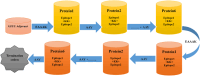
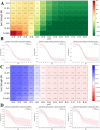
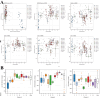
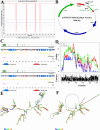
The illness caused by Lactococcus garvieae and Streptococcus iniae is well acknowledged as a disease that results in significant economic losses since it affects a diverse array of fish species. The constraints of existing vaccinations and techniques have prompted the exploration of novel approaches to manage this ailment. Multi-epitope vaccines that use a diverse range of immunogenic proteins have considerable potential. The primary objective of the present research endeavour was to develop a very effective multi-epitope vaccine targeting Streptococcus iniae and Lactococcus garvieae infection in fish. The immunogenic components of Lactococcus garvieae and Streptococcus iniae were used for epitope prediction. A multi-epitope vaccine was constructed using the immunogenic proteins' most effective B cell epitopes and the GFFY adjuvant. Subsequently, an assessment was conducted on many aspects of the developed vaccine, including physicochemical characteristics, antigenicity, secondary structure and tertiary structure. Furthermore, the molecular docking technique was used to study the interaction between the proposed vaccine and its TLR-5 receptor. The nucleotide sequence of the vaccine was subsequently modified to facilitate its expression in Lactococcus lactis. The findings of the current investigation indicate that the vaccine developed exhibited stability, as shown by its molecular weight of 93989.19 Da and antigenicity value of 0.8547. In addition, the study of the vaccine's structure indicated that it consisted of 32.24% alpha helix, with 88.41% of its residues located in the preferred area. The proposed vaccine effectively docked to its TLR5 receptor was shown, resulting in the lowest energy of -995.4. According to the data obtained, the developed vaccine has the potential to effectively prevent infection in fish caused by Lactococcus garvieae and Streptococcus iniae. Our findings suggest that the peptide vaccine might be a favourable choice for prophylaxis against Lactococcus garvieae and Streptococcus iniae.
Keywords: Lactococcus garvieae; Streptococcus iniae; immunoinformatic; multi‐epitope vaccine.
© 2025 The Author(s). Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Designing and Cloning of the Gene Vaccine Carrying the Viral Haemorrhagic Septicaemia Multi-Epitope Gene in the pNZ8121 Secretion Vector.Vet Med Sci. 2025 May;11(3):e70365. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70365. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40294182
-
Valuable method for production of oral vaccine by using alginate and chitosan against Lactococcus garvieae/Streptococcus iniae in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Jul;90:431-439. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.05.020. Epub 2019 May 11. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31082516
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armwood, A. R. , Griffin M. J., Richardson B. M., Wise D. J., Ware C., and Camus A. C. 2022. “Pathology and Virulence of Edwardsiella Tarda, Edwardsiella Piscicida, and Edwardsiella Anguillarum in Channel (Ictalurus punctatus), Blue (Ictalurus furcatus), and Channel × Blue Hybrid Catfish.” Journal of Fish Diseases 45, no. 11: 1683–1698. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ben Hamed, S. , Tapia‐Paniagua S. T., Moriñigo M. Á., and Ranzani‐Paiva M. J. 2021. “Advances in Vaccines Developed for Bacterial Fish Diseases, Performance and Limits.” Aquaculture Research 52, no. 6: 2377–2390.
-
- Brunt, J. , and Austin B.. 2005. “Use of a Probiotic to Control Lactococcosis and Streptococcosis in Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus Mykiss (Walbaum).” Journal of Fish Diseases 28, no. 12: 693–701. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

