Role of Adipose Tissue Compartments for Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Endotypes
- PMID: 40526445
- PMCID: PMC12635897
- DOI: 10.2337/dc24-2023
Role of Adipose Tissue Compartments for Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Endotypes
Abstract
Objective: The severe insulin-resistant diabetes (SIRD) endotype is associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and higher cardiovascular risk. We investigated whether skeletal muscle or adipose tissue lipids are elevated in SIRD.
Research design and methods: Participants (N = 420) of the German Diabetes Study (GDS) were assigned to diabetes clusters using a validated algorithm. 1H-magnetic resonance methods were used to quantify intramyocellular lipids (IMCLs), intrahepatic lipids (IHLs), and visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) volumes.
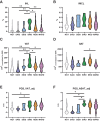
Results: Aside from elevated IHLs (P < 0.01), SIRD showed higher VAT and SAT than other endotypes after adjustment for BMI (all P < 0.05) but not for multiple comparisons. All endotypes featured comparable IMCLs. VAT volume and IHLs correlated with cardiovascular risk scores (Framingham r = 0.661 and 0.548, respectively, P < 0.05). Polygenic risk scores for VAT were associated with higher cardiovascular risk.
Conclusions: SIRD features higher IHLs and nominally higher VAT volume, which likely contribute to increased cardiovascular risk, highlighting implications for tailored prevention and treatment.
© 2025 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Unravelling Diabetes Endotypes and Associated Pathophysiology for Precision Medicine in Diabetes: Ready for Prime Time?Diabetes Care. 2025 Dec 1;48(12):2000-2003. doi: 10.2337/dci25-0067. Diabetes Care. 2025. PMID: 41264839 No abstract available.
References
-
- Xourafa G, Korbmacher M, Roden M. Inter-organ crosstalk during development and progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2024;20:27–49 - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, et al. Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments: association with metabolic risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2007;116:39–48 - PubMed
-
- Wong ND, Sattar N. Cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus: epidemiology, assessment and prevention. Nat Rev Cardiol 2023;20:685–695 - PubMed
-
- Targher G, Corey KE, Byrne CD, Roden M. The complex link between NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus: mechanisms and treatments. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;18:599–612 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

