The Nanocarrier Landscape─Evaluating Key Drug Delivery Vehicles and Their Capabilities: A Translational Perspective
- PMID: 40526827
- PMCID: PMC12232268
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5c07366
The Nanocarrier Landscape─Evaluating Key Drug Delivery Vehicles and Their Capabilities: A Translational Perspective
Abstract
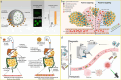
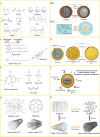
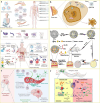
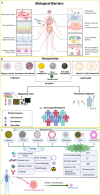
The field of nanomedicine is currently in a revolutionary phase, propelled by the significant potential of nanoparticles, which offer several advantages over traditional drug delivery systems. The purpose of this paper is to aggregate contemporary knowledge of nanoparticles developed and applied in drug delivery across major disease classes. Accordingly, we offer, through a thorough search of the literature, a comprehensive overview of the prevalent nanoparticles used in drug delivery systems, covering polymeric, lipid-based, inorganic, and carbon-based nanoparticles, and discuss their advantages and limitations. This work primarily focuses on studies published in the last 5 years, aiming to provide an up-to-date assessment of the critical nanoparticles in drug delivery. Narratively, we synthesize a comprehensive overview of the state-of-the-art in nanocarrier technology, providing in-depth insights into the key nanoparticle types presented in the contemporary literature, their fundamental benefits, potential clinical applications, and limitations impeding their development and adoption. We note that there are gaps and opportunities for concerted efforts focused on developing biocompatible and biodegradable nanoparticles, establishing scalable and cost-effective manufacturing processes, and addressing regulatory challenges associated with nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. These challenges persist despite the immense translational success of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems and necessitate continued interdisciplinary research and cross-industry collaboration among scientists, clinicians, and regulatory bodies.
Keywords: biocompatibility; nanocarriers; nanoparticle drug delivery; personalized nanomedicine; theranostics; toxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Chamundeeswari M., Jeslin J., Verma M. L.. Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019;17(2):849–865. doi: 10.1007/s10311-018-00841-1. - DOI
-
- Asgari S., Farasati Far B., Charmi G., Maghsoudi P. H., Keihankhadiv S., Seyedhamzeh M., Kaushik A. K.. Chitosan-Grafted-Poly(N-Vinylcaprolactam)-Decorated Fe(3)O(4)@SiO(2) Core-Shell Nanoformulation as an Efficient Drug Delivery System for Poorly Soluble Drugs. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023;6(12):5809–5827. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00924. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

