Immune Subtyping Identifies Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive Early-Stage Breast Cancer Who Respond to Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy (IO): Results From Five IO Arms of the I-SPY2 Trial
- PMID: 40526879
- PMCID: PMC12184982
- DOI: 10.1200/PO-24-00776
Immune Subtyping Identifies Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive Early-Stage Breast Cancer Who Respond to Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy (IO): Results From Five IO Arms of the I-SPY2 Trial
Abstract
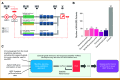
Purpose: Neoadjuvant immunotherapy (IO) has become the standard of care for early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), but not yet for other subtypes. We previously developed a clinical-grade mRNA-based immune classifier (ImPrint) predicting response to IO that is now being used in I-SPY2.2 as part of the response predictive subtypes. We report the performance of ImPrint in hormone receptor-positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HR+HER2-) patients from five IO arms.
Methods: A total of 204 HR+HER2- (MammaPrint high-risk) patients from five IO arms (anti-PD-1, anti-PD-L1/poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase inhibitor combination, anti-PD-1/toll-like receptor 9 dual-IO combination, and anti-PD-1 ± lymphocyte activation gene 3 dual-IO combination) and 191 patients from the chemotherapy-only control arm were included in this analysis. Patients were classified as ImPrint+ (likely sensitive) versus ImPrint- (likely resistant), using pretreatment mRNA. Performance of ImPrint for predicting pathologic complete response (pCR) to IO-containing arms was characterized and compared with tumor grade (III), MammaPrint (ultra) High2 risk (MP2), and estrogen receptor (ER)-low (ER ≤ 10%).
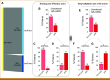
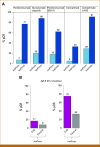
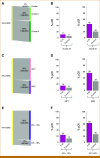
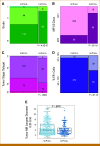
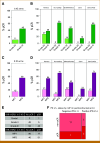
Results: Overall, the pCR rate across the five IO arms was 33%. 26% of HR+HER2- patients were ImPrint+, and pCR rates with IO were 75% in ImPrint+ versus 17% in ImPrint-, with the highest pCR rate >90% in a dual-IO arm. In the control arm, pCR rates were 33% in ImPrint+ and 8% in ImPrint-. Tumor grade (III), MP2, and ER-low showed pCR rates in IO of 45%, 56%, and 63%, respectively, with lower pCR odds ratios (OR < 7.5) compared with ImPrint (OR = 14.5).
Conclusion: Using an accurate selection strategy, HR+HER2- patients could achieve pCR rates similar to what is seen with best neoadjuvant therapies in TNBC and HER2+ (ie, pCR rate >65%-70%). ImPrint, an Food and Drug Administration IDE-enabled assay, may represent a way to identify HR+HER2- patients for IO that best balances likely benefit versus risk of serious immune-related adverse events.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01042379.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathologic complete response (pCR) rates for patients with HR+/HER2- high-risk, early-stage breast cancer (EBC) by clinical and molecular features in the phase II I-SPY2 clinical trial.Ann Oncol. 2025 Feb;36(2):172-184. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.10.018. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Ann Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39477071 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Combined prognostic impact of initial clinical stage and residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant systemic therapy in triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer: an analysis of the I-SPY2 randomized clinical trial.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 23;27(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s13058-025-02070-1. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40551254 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Optimizing neoadjuvant treatment in HER2-positive breast cancer: the role of HER2, HR, PD-L1 expression and regimen selection.Future Oncol. 2025 Aug;21(19):2505-2513. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2526268. Epub 2025 Jun 29. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40583394
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Cardoso F, McArthur HL, Schmid P, et al. : LBA21 KEYNOTE-756: Phase III study of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab (pembro) or placebo (pbo) + chemotherapy (chemo), followed by adjuvant pembro or pbo + endocrine therapy (ET) for early-stage high-risk ER+/HER2– breast cancer. Ann Oncol 34:S1260-S1261, 2023
-
- Loi S, Curigliano G, Salgado RF, et al. : LBA20: A randomized, double-blind trial of nivolumab (NIVO) vs placebo (PBO) with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) followed by adjuvant endocrine therapy (ET) ± NIVO in patients (pts) with high-risk, ER+ HER2− primary breast cancer (BC). Ann Oncol 34:S1259-S1260, 2023
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

