Structure-Guided Design of a KMT9 Inhibitor Prodrug with Cellular Activity
- PMID: 40526927
- PMCID: PMC12257510
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02953
Structure-Guided Design of a KMT9 Inhibitor Prodrug with Cellular Activity
Abstract
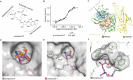
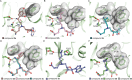
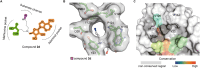
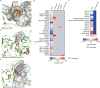
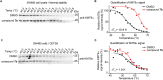
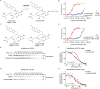
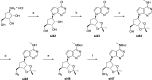
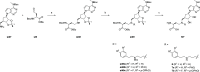
Lysine methyltransferase 9 (KMT9), an obligate heterodimer (KMT9α/KMT9β), belongs to the few described Rossmann-fold histone lysine methyltransferases and monomethylates histone H4 at lysine 12 (H4K12me1). KMT9 depletion or inhibition impairs the proliferation of tumors, including prostate, lung, colon, and bladder cancer cells, underscoring its therapeutic potential. Here, we show the development of branched cofactor analogues with a methionine side chain as highly potent KMT9 inhibitors. Through structure-guided design, a basic nitrogen and 4-chlorophenoxy-2-fluorobenzene in the substrate branch contribute most to the high potency and selectivity. Due to the zwitterionic methionine side chain, the inhibitors did not show cellular activity. Importantly, an ethyl ester prodrug 8 exhibits cellular target engagement and effectively blocks the proliferation of colon cancer cell lines, further validating pharmacological inhibition of KMT9 as a promising strategy for cancer therapy.
Figures
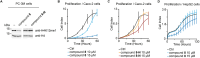
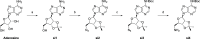
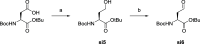

References
-
- Polak P., Karlic R., Koren A., Thurman R., Sandstrom R., Lawrence M., Reynolds A., Rynes E., Vlahovicek K., Stamatoyannopoulos J. A., Sunyaev S. R.. Cell-of-origin chromatin organization shapes the mutational landscape of cancer. Nature. 2015;518(7539):360–364. doi: 10.1038/nature14221. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

