A nitroalkene derivative of salicylate, SANA, induces creatine-dependent thermogenesis and promotes weight loss
- PMID: 40527924
- PMCID: PMC12373507
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-025-01311-z
A nitroalkene derivative of salicylate, SANA, induces creatine-dependent thermogenesis and promotes weight loss
Abstract
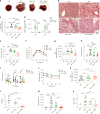
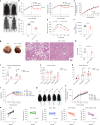
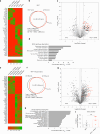
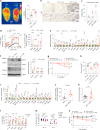
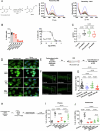
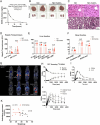
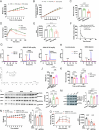
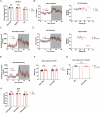
The emergence of glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists represents a notable advancement in the pharmacological treatment of obesity, yet complementary approaches are essential. Through phenotypic drug discovery, we developed promising nitroalkene-containing small molecules for obesity-related metabolic dysfunctions. Here, we present SANA, a nitroalkene derivative of salicylate, demonstrating notable efficacy in preclinical models of diet-induced obesity. SANA reduces liver steatosis and insulin resistance by enhancing mitochondrial respiration and increasing creatine-dependent energy expenditure in adipose tissue, functioning effectively in thermoneutral conditions and independently of uncoupling protein 1 and AMPK activity. Finally, we conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1A/B clinical trial, which consisted of two parts, each with four arms: (A) single ascending doses (200-800 mg) in healthy lean volunteers; (B) multiple ascending doses (200-400 mg per day for 15 days) in healthy volunteers with overweight or obesity. The primary endpoint assessed safety and tolerability. Secondary and exploratory endpoints included pharmacokinetics, tolerability, body weight and metabolic markers. SANA shows good safety and tolerability, and demonstrates beneficial effects on body weight and glucose management within 2 weeks of treatment. Overall, SANA appears to be a first-in-class activator of creatine-dependent energy expenditure and thermogenesis, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic candidate for 'diabesity'. Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry registration: ACTRN12622001519741 .
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: G.V.L., C.B., M.P.G. and C.E. hold shares in EOLO USA Inc. E.N.C. acts as a scientific advisor for EOLO USA Inc. K.C., M.P.G., V.P.-T., M.B., L.S., J.H. and M.I. are used by EOLO USA Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Update of
-
A nitroalkene derivative of salicylate alleviates diet-induced obesity by activating creatine metabolism and non-shivering thermogenesis.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 12:rs.3.rs-3101395. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3101395/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Metab. 2025 Aug;7(8):1550-1569. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01311-z. PMID: 37502859 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Flegal, K. M., Graubard, B. I., Williamson, D. F. & Gail, M. H. Cause-specific excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. JAMA298, 2028–2037 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Wilding, J. P. H. et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N. Engl. J. Med.384, 989–1002 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL-168290/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- 19TPA34850089/American Heart Association (American Heart Association, Inc.)
- R01 AG026094/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128485/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK124510-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HL153532/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM119528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA233790/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL168290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35GM119528/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AG058812/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI144004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NS 112727/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01HL153532/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 HL-128485/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- NS AI144004/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 NS112727/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK124510/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

