Nursing green transformational leadership style, behavioral intentions, actual behavior and creativity: the impact of a green climate
- PMID: 40528183
- PMCID: PMC12172357
- DOI: 10.1186/s12912-025-03331-2
Nursing green transformational leadership style, behavioral intentions, actual behavior and creativity: the impact of a green climate
Abstract
Background: Nursing leaders and nurses play a significant role in promoting green healthcare practices in healthcare organizations. Therefore, it is essential to understand the mechanism through which leadership can affect the green behavior and creativity of nurses.
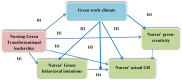
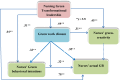
Aims: To investigate the effects of transformational leadership and a green work climate on nurses' behavioral intentions, actual green behavior, and green creativity.
Methods: Self-report questionnaires (nursing green transformational leadership, climate, behavior, and creativity) were used to gather data from 400 nurses.
Results: Nurses' perceptions of nursing green transformational leadership, climate, behavior, and creativity were all at acceptable levels. Regression analysis indicated that nurses' green behavioral intentions, actual green behavior, and green creativity, as well as the green work climate, were positively affected by nursing green transformational leadership. The Sobel results showed that nursing green transformational leadership indirectly affected nurses' green behavioral intentions, actual green behavior and green creativity through the mediating role of the green work environment. There was a moderating influence of the green work climate on the association between nurses' green behavioral intentions and actual green behavior.
Conclusion: A green work climate had a mediating effect on the relationships among nursing green transformational leadership, nurses' green behavioral intentions, actual green behavior and green creativity. Nurses' green behavioral intentions positively affect their actual green behavior through the moderating effects of a green work climate.
Implication: Nurse managers should be aware of the influence of leadership style and the green work climate as significant factors influencing the ability of nurses to engage in green behavior and foster their green creativity.
Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Keywords: Actual green behavior; Environmental behavior intention; Green creativity; Green transformational leadership; Green work climate; Mediating effect; Moderating effect; Nurses; Nursing management.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Approval for conducting the research was obtained from the ethical committee of the Faculty of Medicine at Alexandria University (the IRB number was 0306600) and the Administration of the Faculty of Nursing at Matrouh University. After the purpose of the study was explained, written consent was obtained from the nurses to participate before they completed the questionnaire. All nurses were assured that their responses would not be used in their performance appraisal and would be analyzed with anonymity and confidentiality. The nurses were also informed of their rights to refuse participation and withdraw from the study at any time. All research procedures of present study were performed in adhering to the Declaration of Helsinki and compliance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between transformational leadership, work motivation, and engagement among nurses in Jordanian governmental hospitals.BMC Nurs. 2025 Jul 4;24(1):842. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03518-7. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40616093 Free PMC article.
-
Nurse Managers' Toxic Leadership: Its Relation to Nurses' Internal and External Intentions to Whistleblowing.J Nurs Manag. 2025 Jun 28;2025:1734502. doi: 10.1155/jonm/1734502. eCollection 2025. J Nurs Manag. 2025. PMID: 40656906 Free PMC article.
-
Transformational leadership, psychological empowerment, work engagement and intensive care nurses' job performance: a cross-sectional study using structural equation modeling.BMC Nurs. 2025 Aug 5;24(1):1025. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03685-7. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40764543 Free PMC article.
-
Leadership practices and staff nurses' intent to stay: a systematic review.J Nurs Manag. 2011 May;19(4):461-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2834.2011.01209.x. Epub 2011 Mar 29. J Nurs Manag. 2011. PMID: 21569143
-
Consensus achievement of leadership, organisational and individual factors that influence safety climate: Implications for nursing management.J Nurs Manag. 2018 Jan;26(1):50-58. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12519. Epub 2017 Sep 21. J Nurs Manag. 2018. PMID: 28940765
References
-
- Abourokbah S, Bajaba S, Yaqub MZ. Leading the green wave: how and when green transformational leadership cultivates employee green creativity. Acta Psychol. 2024;250:104503. 10.1016/j.actpsy.2024.104503. - PubMed
-
- Faraz NA, Ahmed F, Xiong X. How firms leverage corporate environmental strategy to nurture green behavior: role of multilevel environmentally responsible leadership. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manage. 2024;31(1):243–59.
-
- Chen YS, Chang CH. The determinants of green product development performance: green dynamic capabilities, green transformational leadership, and green creativity. J Bus Ethics. 2013;116:107–19.
-
- Al-Sawy MMR. Greening the workplace: the power of a positive climate and leader influence on employee behavior. J Bus Res. 2023;45(3):1–45.
-
- Robertson JL, Barling J. Contrasting the nature and effects of environmentally specific and general transformational leadership. Leadersh Organ Dev J. 2017;38:22–41.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources