The role of probiotics in promoting systemic immune tolerance in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 40528248
- PMCID: PMC12172233
- DOI: 10.1186/s13099-025-00702-7
The role of probiotics in promoting systemic immune tolerance in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
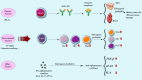
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disorder branded via over-activation of the immune system, resulting in atypical roles of natural and adaptive immune cells and the making of numerous autoantibodies against nuclear components. The causes and pathogenesis of this disease are not completely realized. The gut microbiota plays a significant character in human health and disorder, particularly in autoimmune diseases.Gut microbiome dysbiosis can affect the host immune system as suggested by several recent studies, balance and activity of the gut microbiome, which are influenced by daily diet, might be associated with disease activity in SLE. There are rising signs to support the immunomodulatory abilities of certain probiotics. Numerous investigational and clinical surveys have demonstrated the useful effects of certain probiotic bacteria, mainly strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, in patients with SLE. Various species of bacteria were found to be positively or negatively associated with SLE gut microbiomes. A better comprehension of the Studying the gut microbiota will provide a good opportunity to identify microbes involved in tolerance in systemic lupus patients. The purpose of this study is to review the existing literature on probiotics that have the ability to restore tolerance and modulate the levels of inflammatory or anti-inflammatory cytokines that play a role in SLE.
Keywords: Cytokines; Immune dysregulation; Immunoregulatory probiotics; Microbiota; Probiotic; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Levy M, et al. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(4):219–32. - PubMed
-
- Davidson A, Diamond B. General features of autoimmune disease, in The autoimmune diseases. Elsevier; 2020. pp. 17–44.
-
- Brackmann HH, et al. Immune tolerance induction: what have we learned over time? Haemophilia. 2018;24:3–14. - PubMed
-
- Bieber K, et al. Autoimmune pre-disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2023;22(2):103236. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

