Identification of core genes in acute kidney injury: evidence from multi-omics human transcriptomic data and in vivo models
- PMID: 40529024
- PMCID: PMC12170083
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-2024-677
Identification of core genes in acute kidney injury: evidence from multi-omics human transcriptomic data and in vivo models
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) affects up to 23.2% of hospitalized patients, but its complex pathophysiology hinders diagnosis and treatment. Bioinformatics-driven identification of core genes from large-scale omics data offers a promising approach for uncovering diagnostic and therapeutic targets. This study aims to integrate multi-omics data with experimental validation to identify core genes involved in AKI and explore their mechanisms.
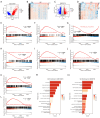
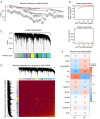
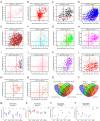
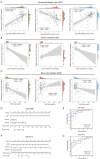
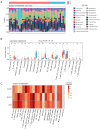
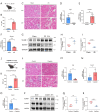
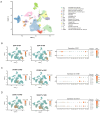
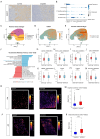
Methods: We analyzed renal transcriptomic data from 67 AKI patients and 20 controls, integrating differential expression, weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), and clinical correlations to identify key genes. A nomogram model was used to assess diagnostic performance, and immune microenvironment characteristics were analyzed using CIBERSORT. AKI was induced in mice by ischemia-reperfusion and cisplatin, with gene expression validated by reverse transcription real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), Western blot, and immunohistochemistry. SUGCT expression and function were further examined in proximal tubules (PT) using human single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) and spatial transcriptomics.
Results: Three core genes, epidermal growth factor (EGF), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM1), and SUGCT, were identified, showing significant associations with AKI phenotypes and clinical renal parameters. Combined, these genes provided a robust diagnostic model for AKI. CIBERSORT associated VCAM1 with monocytes, SUGCT with monocytes and M2 macrophages, and EGF with monocytes and T cells. Both mouse models showed downregulation of Sugct and Egf, and upregulation of Vcam1, consistent with human data. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing revealed that SUGCT was highly expressed in healthy PT but downregulated in severely injured PT. Low SUGCT expression correlated with suppressed mitochondrial functions and activated immune responses. Spatial transcriptomics confirmed that regions of high SUGCT expression co-localized with areas of oxidative phosphorylation activity in PT.
Conclusions: This study highlights three core genes of AKI, especially SUGCT, which is related to mitochondrial metabolism and immune balance in PT during AKI, offering potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury (AKI); SUGCT; inflammation; mitochondria; weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-2024-677/coif). J.N. reports that this work was supported by grants from the Nature and Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82090023 and 82330019), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 2019B1515120075), National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding (Scientific Research Fund of Peking University First Hospital) (No. 2023IR16), and Research Project in State Key Laboratory of Vascular Homeostasis and Remodeling (Peking University) (No. 24QZ003). The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unveiling PANoptosis in Acute Kidney Injury: An Integrative Multi-Dimensional Approach to Identify Key Biomarkers.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jul 2;18:8735-8754. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S525222. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40620603 Free PMC article.
-
Core Neuroinflammatory Pathways Contributing to Delayed Encephalopathy After Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Revealed by Multi-omics and Single Nucleus RNA-Seq.Curr Med Chem. 2025 Jul 7. doi: 10.2174/0109298673407372250623101809. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40626535
-
Apoptosis-related prognostic biomarkers and potential targets for acute kidney injury based on machine learning algorithm and in vivo experiments.Apoptosis. 2024 Apr;29(3-4):303-320. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01896-4. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 37789227
-
Progress and applications of single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptome technology in acute kidney injury research.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025 May 30;36(3):102583. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102583. eCollection 2025 Sep 9. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025. PMID: 40568028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
