Diagnostic value of the combined detection of serum tumor necrosis factor-α and fecal calprotectin in early sepsis-related encephalopathy
- PMID: 40529149
- PMCID: PMC12171133
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1598624
Diagnostic value of the combined detection of serum tumor necrosis factor-α and fecal calprotectin in early sepsis-related encephalopathy
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the value of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and fecal calprotectin in the early diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE).
Methods: We recruited 150 patients with sepsis, admitted from January 2020 to January 2022. Of these, 80 patients had SAE and 70 patients did not. The levels of serum TNF-α and fecal calprotectin of patients while in the intensive care unit were measured and correlated with the acute physiology and chronic health evaluation scoring system II (APACHE II) score, the sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score and 28-day mortality. We examined the value of TNF-α and fecal calprotectin in the diagnosis and prognosis of SAE.
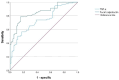
Results: The APACHE II and SOFA scores and 28-day mortality of the SAE group were significantly higher than those of the sepsis group, which indicated that the condition of the SAE group was more critical. In the SAE group, TNF-α and fecal calprotectin levels were positively correlated with the APACHE II and SOFA scores (P < 0.05), which may be related to disease severity. Assessing TNF-α level alongside fecal calprotectin level is highly valuable for the diagnosis of SAE and determining poor prognoses in SAE patients.
Conclusions: TNF-α and fecal calprotectin may be involved in the pathogenesis of SAE. Both have high specificity and sensitivity for early SAE diagnosis. Moreover, they have good predictive value and can serve as prognostic indicators.
Keywords: diagnostic value; early sepsis-related encephalopathy; fecal calprotectin; pathogenesis of SAE; serum tumor necrosis factor-α.
Copyright © 2025 OuYang, Yang, Wu, Liu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The impact of sedation and analgesia scores on prognosis in critically ill sepsis patients with sepsis-associated encephalopathy: a retrospective analysis.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 25;16:1622964. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1622964. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40635709 Free PMC article.
-
Association of serum Netrin-1, NSE, and S100β with brain injury severity and prognosis in patients with sepsis-associated encephalopathy.Biomol Biomed. 2025 Jul 26. doi: 10.17305/bb.2025.12215. Online ahead of print. Biomol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40714984
-
The predictive value of platelet parameters and hemorheological indicators for elderly sepsis patients.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Aug 2;25(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-03222-8. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40753373 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal administration of progestogens for preventing spontaneous preterm birth in women with a multiple pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 20;2019(11):CD012024. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012024.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31745984 Free PMC article.
-
Defining disease severity in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis for the application to biomarker research: an interdisciplinary perspective.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):14-23. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae080. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38419411 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yu D, Unger D, Unge C, Parke A, Sunden-Cullberg J, Stralin K, et al. Correlation of clinical sepsis definitions with microbiological characteristics in patients admitted through a sepsis alert system; a prospective cohort study. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. (2022) 21:7. 10.1186/s12941-022-00498-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li XL, Xie JF, Ye XY, Li Y, Li YG, Feng K, et al. Value of cerebral hypoxic-ischemic injury markers in the early diagnosis of sepsis associated encephalopathy in burn patients with sepsis. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. (2022) 38:21–8. 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20211006-00346 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

