ToxiPep: Peptide toxicity prediction via fusion of context-aware representation and atomic-level graph
- PMID: 40529180
- PMCID: PMC12171765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.05.039
ToxiPep: Peptide toxicity prediction via fusion of context-aware representation and atomic-level graph
Abstract
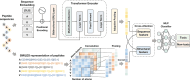
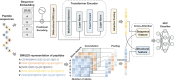
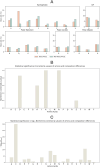
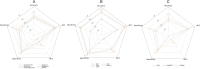
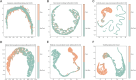
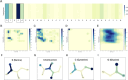
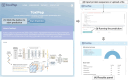
Peptide-based therapeutics have emerged as a promising avenue in drug development, offering high biocompatibility, specificity, and efficacy. However, the potential toxicity of peptides remains a significant challenge, necessitating the development of robust toxicity prediction methods. In this study, we introduce ToxiPep, a novel dual-model framework for peptide toxicity prediction that integrates sequence-based contextual information with atomic-level structural features. This framework combines BiGRU and Transformer to capture local and global sequence dependencies while leveraging multi-scale CNNs to extract refined structural features from molecular graphs derived from peptide SMILES representations. A cross-attention mechanism aligns and fuses these two feature modalities, enabling the model to capture intricate relationships between sequence and structural information. ToxiPep outperforms several state-of-the-art tools, including ToxinPred2, CSM-Toxin, PepNet, and ToxinPred3, on both internal and independent test sets. Additionally, interpretability analyses reveal that ToxiPep identifies key amino acids along with their structural features, providing insights into the molecular mechanisms of peptide toxicity. To facilitate broader accessibility, we have also developed a web server for convenient user access. Overall, this framework has the potential to accelerate the identification of safer therapeutic peptides, offering new opportunities for peptide-based drug development in precision medicine.
Keywords: Deep learning; Drug discovery; Peptide bioactivity prediction; Sequence modeling.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Research Network of Computational and Structural Biotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
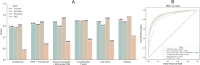
Similar articles
-
Multistage attention-based extraction and fusion of protein sequence and structural features for protein function prediction.Bioinformatics. 2025 Jul 1;41(7):btaf374. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf374. Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40569190 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction, screening and characterization of novel bioactive tetrapeptide matrikines for skin rejuvenation.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):92-106. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae061. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38375775
-
Integrating Gut Microbiome and Metabolomics with Magnetic Resonance Enterography to Advance Bowel Damage Prediction in Crohn's Disease.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jun 11;18:7631-7649. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S524671. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40535353 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining disease severity in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis for the application to biomarker research: an interdisciplinary perspective.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):14-23. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae080. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38419411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exo-Tox: Identifying Exotoxins from secreted bacterial proteins.BioData Min. 2025 Aug 8;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13040-025-00469-2. BioData Min. 2025. PMID: 40781630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Craik David J., Fairlie David P., Liras Spiros, Price David. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2013;81(1):136–147. - PubMed
-
- Rastogi Shruti, Shukla Shatrunajay, Kalaivani M., Singh Gyanendra Nath. Peptide-based therapeutics: quality specifications, regulatory considerations, and prospects. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24(1):148–162. - PubMed
-
- Haggag Yusuf A., Donia Ahmed A., Osman Mohamed A., El-Gizawy Sanaa A. Peptides as drug candidates: limitations and recent development perspectives. Biomed J. 2018;1(3)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
