The Negative Regulatory Role of Transcriptional Regulator H-NS on the Type VI Secretion System in Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 40529232
- PMCID: PMC12170815
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S512650
The Negative Regulatory Role of Transcriptional Regulator H-NS on the Type VI Secretion System in Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
Introduction: This study investigates the negative regulatory role of the global transcriptional regulator H-NS (Histone-like Nucleoid Structuring Protein) on the Type VI secretion system (T6SS) in Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii). We explored potential targets of H-NS mediated silencing or activation within the regulation of A. baumannii T6SS, along with the specific regulatory mechanisms involved, thereby providing a theoretical foundation for further research on A. baumannii invasive infections stemming from mixed infections and the development of therapeutic target.
Methods: Using the plasmids pAT04 and pYMAb2-hyg, we constructed A. baumannii ATCC19606 strains with the hns gene knocked out (ABΔhns) and overexpressed (ABhns+). We measured the expression of the T6SS-related gene hcp in wild-type (AB WT), ABΔhns, and ABhns+ strains using RT-qPCR, combined with a mouse sepsis model featuring mixed infections. We assessed their serum resistance, competitive ability against Escherichia coli (E. coli), and blood invasion capability. Proteomic analysis identified differentially expressed proteins, and we further investigated the regulatory role of H-NS on A. baumannii T6SS using electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA).
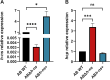
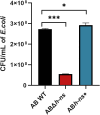
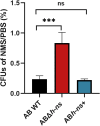
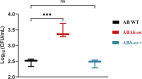
Results: We successfully constructed both ABΔhns and ABhns+ strains of A. baumannii ATCC19606. RT-qPCR results indicated that H-NS functions as a negative regulator of the T6SS-related gene hcp in A. baumannii. Phenotypic assays for extracellular virulence revealed that the loss of hns enhanced both the competitive ability and serum resistance of ATCC19606. Results from the mouse sepsis infection model demonstrated that knockout of hns significantly increased the bacterium's blood invasion capability. Bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed proteins identified elevated levels of T6SS-related proteins in the knockout strain. Furthermore, EMSAs confirmed that H-NS directly binds to multiple sites in the upstream region of hcp.
Conclusion: H-NS inhibits the expression of T6SS-related proteins in A. baumannii by regulating relevant targets associated with the T6SS. This regulation influences the bacterium's pathogenicity, interspecies competitive ability, and serum resistance.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; H-NS; mixed infection; septicemia; type VI secretion system.
© 2025 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

