Genetic analysis using long-read sequencing to overcome the difficulties in VWF gene
- PMID: 40529342
- PMCID: PMC12173654
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpth.2025.102888
Genetic analysis using long-read sequencing to overcome the difficulties in VWF gene
Abstract
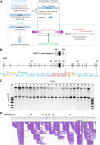
Background: Genetic defects in von Willebrand factor (VWF) can lead to von Willebrand disease (VWD). Identifying causative or modifier variants of VWF is crucial for the diagnosis, classification, and clinical management of VWF disorders. However, owing to the length (178 kb) and complexity of VWF and the presence of the pseudogene VWFP1, Sanger sequencing or short-read next-generation sequencing is often challenging.
Objectives: This study aimed to establish a long-read sequencing method using Oxford nanopore technology (ONT) to overcome difficulties associated with VWF gene analysis.
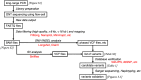
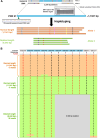
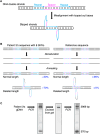
Methods: Genetic analyses were established using genomic DNA from a healthy donor and validated using 3 VWF disorder patient samples. Long-range (∼15 kb) polymerase chain reaction was optimized to obtain 21 amplicons covering the entire VWF gene, avoiding unwanted amplification due to repetitive sequences and VWFP1. ONT nanopore sequencing data were analyzed using software programs, including Clair3, Longshot, and Sniffles. The identified candidate variants were verified by several approaches such as Sanger sequencing and haplotyping.
Results: The entire VWF gene was successfully read using ONT nanopore sequencing, with >200 variants called in each patient sample. A rare missense variant, p.(Gln2442His) and a rare 2599 bp deletion were identified in patients 2 and 3, respectively. However, the deletion was confirmed as long-range polymerase chain reaction artifacts, which warrant attention when using this method.
Conclusion: This study presents an optimal solution using ONT nanopore sequencing to identify variants in VWF, which may improve the diagnosis of VWF disorders.
Keywords: nanopore sequencing; polymerase chain reaction; von Willebrand disease; von Willebrand factor.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Lenting P.J., Christophe O.D., Denis C.V. von Willebrand factor biosynthesis, secretion, and clearance: connecting the far ends. Blood. 2015;125:2019–2028. - PubMed
-
- de Jong A., Eikenboom J. Von Willebrand disease mutation spectrum and associated mutation mechanisms. Thromb Res. 2017;159:65–75. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

