IFN-γ gene polymorphisms +874 T/A and +2109 A/G are associated with the serofast state after early syphilis treatment: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 40529360
- PMCID: PMC12171201
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602527
IFN-γ gene polymorphisms +874 T/A and +2109 A/G are associated with the serofast state after early syphilis treatment: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Background: In approximately 20% of patients with early syphilis, the classical serological response pattern is absent following treatment. They experience a serofast state, which manifests as less than a 4-fold decline in non-treponemal titres, without any clinical signs of treatment failure or reinfection. The effectiveness of the immune defense against T. pallidum, as well as its potential failure and the occurrence of the serofast state, depends on the Th1 cellular response, including cytokines such as IFN-γ. The aim of this prospective observational study was to investigate the impact of IFN-γ gene polymorphisms on the occurrence of the serofast state.
Materials and methods: A cohort of 97 patients with early syphilis (73.2% secondary syphilis, 26.8% early latent syphilis) and 50 healthy volunteers were enrolled. Two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the IFN-γ gene promoter region, +874 T>A (rs2430561) and +2109 A>G (rs1861494), were analyzed. Serum IFN-γ levels were measured at baseline, prior to treatment. Patients were stratified into serofast (n=18) and serologically cured (n=79) groups.
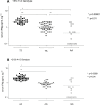
Results: Serofast patients exhibited significantly lower baseline serum IFN-γ levels compared to the serologically cured group (p=0.01). All healthy subjects had IFN-γ levels below the detection limit. Analysis of IFN-γ gene polymorphisms revealed a significant association with treatment outcomes. The +874 AA and +2109 GG genotypes, associated with low IFN-γ production, were significantly more frequent in serofast patients (p=0.0004 and p=0.002, respectively), with odds ratios (OR) of 7.1 (95% CI: 2.2-23.2) and 5.5 (95% CI: 1.8-17.3), respectively. Additionally, carriers of the +874A/+2109G haplotype were significantly more likely to remain serofast (OR 4.4, p=0.01). Conversely, the +874 TT and +2109 AA genotypes, associated with high IFN-γ production, were significantly linked to serological cure (OR 4.4, p=0.03; OR 4.4, p=0.01). Similarly, the +874T/+2109A haplotype was strongly associated with serological cure (OR 17.9, p<0.0001).
Discussion: Distinct IFN-γ polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with serological outcomes in syphilis. The +874 T>A and +2109 A>G variants influence IFN-γ levels, potentially modulating the immune response and serological recovery. These findings suggest a genetic predisposition underlying serofast syphilis and underscore the importance of personalized approaches in its management.
Keywords: +2109 A/G; +874 T/A; IFN-γ; SNP; polymorphism; serofast state; syphilis.
Copyright © 2025 Kaminiów, Kiołbasa and Pastuszczak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Workowski KA, Berman S, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) . Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2010. MMWR Recomm Rep. (2010) 59:1–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical