Conversion study of hepatocellular carcinoma using HAIC combined with lenvatinib and PD-1/L1 immunotherapy under the guidance of BCLC staging
- PMID: 40529364
- PMCID: PMC12171213
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1596864
Conversion study of hepatocellular carcinoma using HAIC combined with lenvatinib and PD-1/L1 immunotherapy under the guidance of BCLC staging
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) combined with lenvatinib and immunotherapy and explore its potential as a conversion treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC).
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on clinical data from patients with uHCC who underwent HAIC, lenvatinib, and PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy. Data were collected from our hospital between November 2018 and December 2022. Efficacy was assessed based on the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST). The primary endpoints were overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and conversion therapy rate. Additionally, survival status curves were plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method. Lastly, prognostic risk factors affecting conversion therapy and survival outcomes were evaluated using Logistic and Cox regression models.
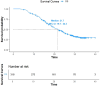
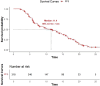
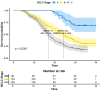
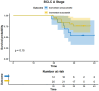
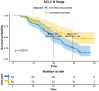
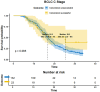
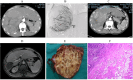
Results: As of December 2022, 318 patients were included, comprising 40 patients (12.6%) in BCLC stage A, 123 patients (38.7%) in BCLC stage B, and 155 patients (48.7%) in BCLC stage C. The overall objective response rate (ORR) was 47.1%, whilst the disease control rate (DCR) was 85.5%. Meanwhile, the median overall survival (mOS) for the entire cohort was 21.7 months (95% CI: 19.7-24.3), with a median progression-free survival (mPFS) of 11.4 months (95% CI: 9.4-13.4). A total of 110 patients (34.6%) underwent conversion surgery. Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified BCLC stage as the sole independent risk factor affecting eligibility for conversion therapy. Subgroup analysis revealed that BCLC-B stage patients who achieved successful conversion therapy demonstrated significantly superior outcomes compared to those who did not undergo successful conversion therapy (median OS: 29.3 months [95% CI: 24.3-NA] vs. 19.7 months [95% CI: 17.2-24.6], P = 0.0013). Multivariate regression analysis identified the BCLC stage, the presence of distant metastasis, and receipt of conversion therapy as independent prognostic factors influencing OS. Among the cohort, 169 (53.1%) experienced grade 3-4 adverse events (AEs), with the most commonly reported AEs being fatigue, fever, and pain.
Conclusion: The combination of HAIC with lenvatinib and immunotherapy yielded a high ORR, improved the conversion therapy rate, and prolonged both OS and PFS in patients with uHCC while maintaining a favorable safety profile. BCLC stage was identified as an independent prognostic factor influencing the success of conversion therapy, with patients in stage B deriving significant survival benefits post-conversion.
Keywords: conversion; hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy; immunotherapy; lenvatinib; unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhao, Gao, Si, Zou, Yang, Xing and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lenvatinib combined with anti-PD-1 antibodies plus locoregional treatment for initial unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a multicenter real-world study.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 10;25(1):1162. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14543-9. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40640796 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of TACE combined with lenvatinib and PD-1 Inhibitor in intermediate-stage HCC exceeding the up-7 criteria: a retrospective cohort study.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 12;16:1560750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1560750. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40574843 Free PMC article.
-
Lenvatinib versus bevacizumab when combined with PD-1/L1 inhibitor and hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 May 23;16:1573098. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1573098. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40486515 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of HAIC-FOLFOX Plus Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors as First-line Treatment for Unresectable Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Acad Radiol. 2025 Aug;32(8):4595-4606. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.09.061. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39384510
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 combination therapy in first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC: an updated systematic review and network meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Oct;26(10):2488-2502. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03442-3. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38625495
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

