The comparison of efficacy and safety between cadonilimab (PD-1/CTLA-4) and anti-PD-1 inhibitors in patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer: a retrospective real-world study
- PMID: 40529375
- PMCID: PMC12171111
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1582299
The comparison of efficacy and safety between cadonilimab (PD-1/CTLA-4) and anti-PD-1 inhibitors in patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer: a retrospective real-world study
Abstract
Introduction: Cadonilimab provides substantial clinical benefits in recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer (R/M CC) in several clinical trials and meeting abstracts. However, the efficacy of cadonilimab in patients with prior failure of anti- programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) inhibitors, as well as a direct comparison of its efficacy and safety with anti-PD-1 inhibitors, has not been reported in real-world settings.
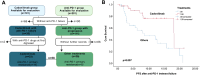
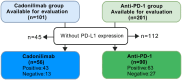
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study at our hospital, including two R/M CC patient cohorts. The first cohort consisted of 101 patients who received cadonilimab, either as monotherapy or in combination with other therapies, between July 1, 2022, and October 31, 2024. The second cohort comprised 201 patients who were treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors (alone or in combination) but did not receive cadonilimab, between August 1, 2018, and March 31, 2024. In cadonilimab group, 4 patients received monotherapy, 13 patients received radiotherapy or surgery, 72 patients received concurrent chemotherapy, 57 patients received targeted therapy. Among anti-PD-1 group, 6 patients received monotherapy, 34 patients received radiotherapy or surgery, 127 patients received concurrent chemotherapy, 116 patients received targeted therapy. Clinicopathologic information, peripheral blood markers and treatment regimens were collected and analyzed to identify prognostic factors of cadonilimab through response rate comparison, as well as univariate, and multivariate analyses. The objective response rate (ORR) was compared between the cadonilimab and anti-PD-1 groups, stratified by PD-L1 expression. Safety data were also analyzed.
Results: The cadonilimab group achieved an ORR of 59.41%, while the anti-PD-1 inhibitors group had an ORR of 44.28%. R/M CC patients with squamous cell carcinoma independently predicted prolonged progression-free survival (p=0.010). In patients with squamous cell carcinoma, the ORR was 60.32% in the cadonilimab group compared to 48.34% in the anti-PD-1 group. Cadonilimab was associated with a survival benefit in patients who had previously failed anti-PD-1 treatment (p=0.007), and showed a significantly higher ORR than anti-PD-1 inhibitors in patients with negative PD-L1 expression (69.23% vs 33.33%, p=0.033). The occurrence of immune related adverse events (irAEs) appeared to be associated with longer medication cycles, while severe adverse reactions were linked to shorter cycles. In addition, the cadonilimab group had a higher cumulative incidence of irAEs, including severe irAEs (12.87% vs. 1.99%, p=0.001), multi-organ irAEs, dyspnea and hypothyroidism than anti-PD-1 inhibitors group.
Conclusion: Cadonilimab improved survival in R/M CC patients with previous anti-PD-1 treatment failure, achieving higher ORR in patients with negative PD-L1 expression compared to ati-PD-1 inhibitors. However, this benefit was associated with a notable increase in irAEs.
Keywords: anti-PD-1; anti-PD-1/CTLA-4; cadonilimab; cervical cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitor.
Copyright © 2025 Pan, Huang, Wan, Huang, He, Xu, Chen, Yin, Li and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures