Modulation of cerebral cortex activity by acupuncture combined with continuous theta-burst stimulation in post-stroke upper limb spasticity: an fNIRS study
- PMID: 40529436
- PMCID: PMC12171123
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1542489
Modulation of cerebral cortex activity by acupuncture combined with continuous theta-burst stimulation in post-stroke upper limb spasticity: an fNIRS study
Abstract
Objective: To observe the modulation and clinical efficacy of acupuncture combined with continuous theta-burst stimulation (cTBS) on cerebral cortical activity in post-stroke upper limb spasticity.
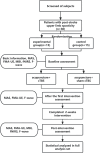
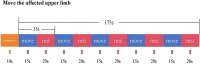
Methods: Patients with upper limb spasticity after stroke were randomly divided into two groups. The control group (n = 15) received acupuncture treatment, and the experimental group (n = 15) received cTBS treatment of the premotor cortex of the healthy side in addition to acupuncture. The efficacy was evaluated before and after the first treatment and 2 weeks after treatment. MAS, FMA, MBI, fNIRS and F wave evaluation were observed in the two groups.
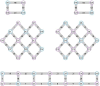
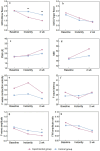
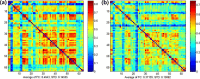
Results: After treatment, there were significant differences between the two groups in MAS, FMA-UE, MBI, F-wave amplitude, and the F/M amplitude ratio index of the experimental group (p < 0.05). Comparison between groups, the MAS-elbow flexor in the experimental group decreased significantly after the first treatment and 2 weeks after treatment. After 2 weeks of treatment, the HbO2 concentration in the CH4 channel exercise phase in the experimental group increased compared with the control group (p FDR <0.05). The strength of functional connection in the left primary motor area (M1)-the left primary somatosensory cortex (S1), the left S1-the right premotor cortex and supplementary motor area (PMC & SMA), and the left S1-the left PMC&SMA showed an increasing trend (0.05 < p FDR < 0.1). The F wave amplitude was significantly lower than before intervention, and the difference was significant (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Acupuncture combined with cTBS can relieve upper limb spasticity, enhance motor function, improve daily living ability, and reduce excessive spinal cord excitability. It can also increase HbO2 concentration in the cerebral cortex. However, large-sample studies are still needed to prove the effect of this therapy on brain networks.
Significance: This study provides evidence for the potential of combined cTBS and acupuncture in stroke rehabilitation.
Clinical trial registration: identifier ChiCTR2400083631.
Keywords: F-wave; acupuncture; continuous theta burst stimulation; fNIRS; spasticity; stroke.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang, Chen, Fan, Sun, Wang, Cong, Yu and Qian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Clinical efficacy observation of repetitive magnetic stimulation for treating upper limb spasticity after stroke.Sci Rep. 2025 May 22;15(1):17722. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02443-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40399427 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dual-tDCS combined with sensorimotor training promotes upper limb function in subacute stroke patients: A randomized, double-blinded, sham-controlled study.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Apr;30(4):e14530. doi: 10.1111/cns.14530. Epub 2023 Nov 23. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37994674 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Clinical observation on jingjin needling combined with rehabilitation training in patients with post-stroke spastic paralysis].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025 Jun 12;45(6):717-722. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20240312-k0002. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40518772 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Is acupuncture combined with repeated transcranial magnetic stimulation more effective in improving upper limb motor dysfunction after stroke? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 2;16:1575879. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1575879. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40529441 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effects of transcranial direct current stimulation combined with different rehabilitation interventions on motor function in people suffering from stroke-related symptoms: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1586685. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1586685. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40534746 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

