Safinamide as an adjunct to levodopa monotherapy in Asian patients with Parkinson's disease experiencing early wearing-off: a pooled analysis of the J-SILVER and KEEP studies
- PMID: 40529448
- PMCID: PMC12171447
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1591664
Safinamide as an adjunct to levodopa monotherapy in Asian patients with Parkinson's disease experiencing early wearing-off: a pooled analysis of the J-SILVER and KEEP studies
Abstract
Background: Limited trials are evaluating the efficacy of monoamine oxidase B inhibitors as an adjunct to levodopa monotherapy for early wearing-off in Parkinson's disease (PD). We evaluated the efficacy and safety of safinamide in patients with fluctuating PD treated with levodopa monotherapy.
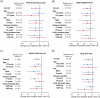
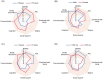
Methods: This pooled analysis used data from the J-SILVER and KEEP studies and targeted patients with PD experiencing wearing-off who received safinamide as adjunct to levodopa monotherapy. Efficacy endpoints were mean changes in 39-item Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire (PDQ-39), Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) Parts III and IV, and daily OFF time at 18 weeks of treatment.
Results: Of 54 patients (J-SILVER, N = 24; KEEP, N = 30), 41 completed the studies. Although not statistically significant, the change in PDQ-39 Summary Index exceeded the minimal clinical important difference (mean [standard deviation (SD)]: -2.2 [7.5], p = 0.094) at Week 18. Significant improvements in MDS-UPDRS Parts III and IV scores and daily OFF time were observed at Week 18 from baseline (mean [SD]: -2.8 [8.5]; p = 0.043, -1.3 [2.7]; p = 0.004, and -1.2 [3.5] hours; p = 0.041, respectively). Adverse events occurred in 24 patients (43.6%) and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) occurred in 12 patients (21.8%). ADRs with an incidence ≥5% were dyskinesia (3 events, 5.5%). In subgroup analyses, improvements in PDQ-39 Summary Index and MDS-UPDRS Parts III and IV were significant in patients aged ≥75 years (p = 0.039, p = 0.029, and p = 0.025, respectively).
Conclusion: Safinamide as an adjunct to levodopa monotherapy was effective for early wearing-off without any new tolerability concerns. Safinamide was particularly beneficial in elderly patients.
Keywords: MAO-B inhibitor; Parkinson’s disease; early wearing-off; elderly; safinamide; sodium channel blocker.
Copyright © 2025 Nishikawa, Kwon, Kogo, Hatano, Cho, Kobayashi, Shiiba, Kim, Ishida, Baik and Hattori.
Conflict of interest statement
NN, D-YK, JC, and JB received consultation fees related to this analysis. TH reports honoraria from Eisai Co., Ltd. during the conduct of the study. YK, CK, HS, and TI are employees of Eisai Co., Ltd. JK is an employee of Eisai Korea Inc. NH reports honoraria, consultation fees, and grants from Eisai Co., Ltd. during the conduct of the study. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safinamide as adjunctive therapy to levodopa monotherapy for patients with Parkinson's disease with wearing-off: The Japanese observational J-SILVER study.J Neurol Sci. 2024 Jun 15;461:123051. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2024.123051. Epub 2024 May 17. J Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38788287
-
Efficacy and safety of safinamide in Parkinson's disease patients with motor fluctuations without levodopa dosage escalation over 18 weeks: KEEP study.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2025 Mar;132(3):431-441. doi: 10.1007/s00702-024-02851-6. Epub 2024 Nov 14. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2025. PMID: 39540934 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and Safety of Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for Early Parkinson's Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis.Eur Neurol. 2024;87(5-6):273-290. doi: 10.1159/000541315. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Eur Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39278214
-
Opicapone for the treatment of early wearing-off in levodopa-treated Parkinson's disease: pooled analysis of patient level data from two randomized open-label studies.J Neurol. 2024 Oct;271(10):6729-6738. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12614-8. Epub 2024 Aug 21. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39164557 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Systematic Review on Parkinson's Disease Medications, Emphasizing on Three Recently Approved Drugs to Control Parkinson's Symptoms.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Dec 30;19(1):364. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010364. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 35010624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radad K, Moldzio R, Krewenka C, Kranner B, Rausch W-D. Pathophysiology of non-motor signs in Parkinson’s disease: some recent updating with brief presentation. Explor Neuroprot Ther. (2023) 3:24–46. doi: 10.37349/ent.2023.00036, PMID: - DOI
-
- Seki M, Kawata Y, Hayashi A, Arai M, Fujimoto S. Prescribing patterns and determinants for elderly patients with Parkinson’s disease in Japan: a retrospective observational study using insurance claims databases. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1162016. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1162016, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lees A, Tolosa E, Stocchi F, Ferreira JJ, Rascol O, Antonini A, et al. Optimizing levodopa therapy, when and how? Perspectives on the importance of delivery and the potential for an early combination approach. Expert Rev Neurother. (2023) 23:15–24. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2023.2176220, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

