Identification of compounds to promote diabetic wound healing based on transcriptome signature
- PMID: 40529493
- PMCID: PMC12171139
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1576056
Identification of compounds to promote diabetic wound healing based on transcriptome signature
Abstract
Purpose: Diabetic wounds are characterized by delayed healing, and the resulting diabetic foot ulcer may lead to severe complications, including amputations and mortality. This study aimed to identify potential small molecule drug candidates that can enhance diabetic wound healing through integrating transcriptome signature and experimental validation strategies.
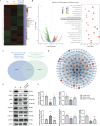
Method: Gene expression dataset (GSE147890) from a diabetic skin humanized mice model in the Gene Expression Omnibus database was analyzed to identify differentially expressed genes between diabetic and normal skin, as well as the wound edge at 24 h. The DEGs were integrated with wound-related genes from the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database to construct a diabetes-specific wound gene profile. Then, the expression signatures were analyzed using the ClusterProfiler package in R for Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses. Hub genes were identified through the String database and Cytoscope software. The Connectivity Map (CMap) was employed to predict compounds with potential therapeutic effects on diabetic wound healing. These predications were validated through in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Results: A total of 167 DEGs were identified between diabetic and normal wounds, with significant enrichment in biological processes related to the extracellular matrix and collagen. The top ten hub genes were predominantly associated with collagen synthesis and inflammatory responses. CMap analysis identified 12 small-molecule compounds, top four of which were further investigated. In vitro experiments demonstrated that two compounds promoted fibroblast proliferation. In vivo studies revealed that compound CG-930 enhanced early inflammatory responses and upregulated the Nod-like receptor signaling pathway, significantly improving wound healing in streptozotocin (STZ) -induced diabetic mice.
Conclusion: This study highlights the altered expression profiles associated with delayed diabetic wound healing, including reduced inflammation and collagen production. Further drug screening identified compound CG-930 as a novel therapeutic agent with significant potential to promote wound healing in diabetic conditions.
Keywords: bioinformatics; diabetic wound; drug discovery; mechanism; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2025 Shang, Liu, Liang, Yin, Yang, Ye, Du and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Revealing the Multi-Target Mechanisms of Fespixon Cream in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing: Integrated Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Clinical RT-qPCR Validation.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jun 25;47(7):485. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070485. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40728954 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of shared key genes and pathways in osteoarthritis and sarcopenia patients based on bioinformatics analysis.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Mar 28;50(3):430-446. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2025.240669. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40628511 Chinese, English.
-
Molecular feature-based classification of retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a prospective cohort study.Elife. 2025 May 23;14:RP100887. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100887. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40407808 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Telemedicine on Wound-Related and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Wounds: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2025 Jun 10;13:e58553. doi: 10.2196/58553. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2025. PMID: 40493508 Free PMC article.
-
Defining disease severity in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis for the application to biomarker research: an interdisciplinary perspective.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):14-23. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae080. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38419411 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

