An artificial intelligence-aided scoping review of medicinal plant research in the Fertile Crescent
- PMID: 40529497
- PMCID: PMC12171211
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1542709
An artificial intelligence-aided scoping review of medicinal plant research in the Fertile Crescent
Abstract
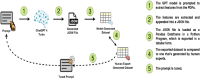
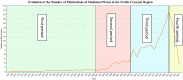
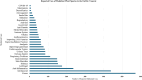
Traditional Arabic and Islamic Medicine (TAIM) originated in the seventh century, but unlike Chinese and Ayurvedic knowledge, TAIM has not evolved through evidence-based research and commercialization. Today, while global interest in traditional medicine is growing, TAIM ancestral knowledge remains unknown and unexplored. The purpose of this study is to provide baseline information on the status of TAIM research to guide future research and contribute to the growth of the sector. The focus of the study is the Fertile Crescent, a region of the Arab World endowed with a rich and diverse eco-geography. The method adopted was a scoping review following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines. The databases used included the Arab World Research Source: Al Masdar, CAB Direct, Iraqi Academic Scientific Journals, MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar. The timeline of the search spanned from the database inception date to June 2024. The search led to 10,171 records which were subsequently reduced to 1,990 publications after deleting duplicates and performing a two-stage screening. Artificial intelligence (AI) technology was used to analyze the data focusing on reported plant species, treatment applications, study types and countries. The Generative Pretrained Transformer 4 (GPT-4) Turbo, a large language model, was used to extract the key features and the results were validated by the researchers. The findings revealed that the types of studies were mostly laboratory-based (86%), while few studies (14%) were field based. The top five treatment applications include cancer (29%), bacterial infections (22%), inflammation (12%), fungal infections (9%), and diabetes (8%). The most notable plant species that were under investigation in the various studies were Nigella sativa L. (Ranunculaceae), Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Lamiaceae), Salvia fruticosa Mill (Lamiaceae), Teucrium polium L. (Lamiaceae), and Thymus vulgaris L. (Lamiaceae). In this review we discuss our findings which suggest potential avenues for further developing TAIM research and exploring the development of botanical drugs. Our findings also revealed that the number of ethnobotanical studies was limited suggesting an urgent need to prevent the loss of ancestral knowledge by formalizing it through evidence-based research and policy guidelines. Addressing these gaps through interdisciplinary collaboration and improved data-sharing mechanisms will be crucial for advancing TAIM research and medicinal plants.
Keywords: Arab medicine; Fertile Crescent; Islamic medicine; herbal medicine; medicinal plants; pharmacology, artificial intelligence.
Copyright © 2025 Al-Sammarraie, Al Mubasher, Awad, Naalbandian, Darwiche, Zurayk, Romani and Talhouk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arabic Aphasia Research Through a Clinical and Linguistic Lens: A Systematic Review of Current Limitations and Future Directions.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 Jul-Aug;60(4):e70064. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.70064. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 40522296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Large Language Models in the Field of Suicide Prevention: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 23;27:e63126. doi: 10.2196/63126. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39847414 Free PMC article.
-
Computer especially AI-assisted drug virtual screening and design in traditional Chinese medicine.Phytomedicine. 2022 Dec;107:154481. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154481. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36215788
-
Use of Augmented Reality for Training Assistance in Laparoscopic Surgery: Scoping Literature Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 28;27:e58108. doi: 10.2196/58108. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39874568 Free PMC article.
-
Surveillance for Violent Deaths - National Violent Death Reporting System, 50 States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico, 2022.MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025 Jun 12;74(5):1-42. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7405a1. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025. PMID: 40493548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd Al-Behadili W. A., Faaz R. A., Tarmooz A. A. (2019). Antifungal activity of Carum carvi L. Extraction against candidia albican and aspergillus Niger. Plant Arch. 19, 1799–1805.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources