Combining a rhesus cytomegalovirus/SIV vaccine with a neutralizing antibody to protect against SIV challenges in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 40529575
- PMCID: PMC12171355
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1592647
Combining a rhesus cytomegalovirus/SIV vaccine with a neutralizing antibody to protect against SIV challenges in rhesus macaques
Abstract
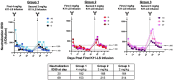
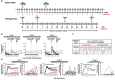
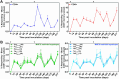
A vaccine is considered essential for controlling the HIV pandemic and ultimately eradicating AIDS. Neutralizing antibodies and MHC-E-restricted CD8+ T cells have shown the ability to protect against the simian counterpart of HIV, SIV, in rhesus macaques. In this study, we provide preliminary evidence that combining these orthogonal antiviral mechanisms can offer increased protection against SIV. Specifically, the replication arrest observed following vaccination with a rhesus cytomegalovirus (RhCMV/SIV)-based vaccine was enhanced by the presence of a passively administered neutralizing antibody at incompletely protective levels. This report encourages studies involving larger cohorts of macaques and alternative methods for administering neutralizing antibodies.
Keywords: HIV; SIV; T cells; neutralizing antibodies; non-human primate (macaque); vaccine.
Copyright © 2025 Coppola, Parren, Bastidas, Saye, Malvin, Jardine, Gilbride, Ojha, Feltham, Morrow, Barber-Axthelm, Bochart, Fast, Oswald, Shoemaker, Lifson, Picker, Burton and Hansen.
Conflict of interest statement
LP and SH have a financial interest in Vir Biotechnology, Inc., a company that may have a commercial interest in the results of CMV vector research and technology. This potential conflict of interest has been reviewed and managed by OHSU. RF, KO, RS, and JL were employed by Leidos Biomedical Research, Inc. DB is a consultant for IAVI. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Update of
-
Combining a rhesus cytomegalovirus/SIV vaccine with neutralizing antibody to protect against SIV challenge in rhesus macaques.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 1:2025.03.20.644395. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.20.644395. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 02;16:1592647. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1592647. PMID: 40196580 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bolton D. L., Pegu A., Wang K., Mcginnis K., Nason M., Foulds K., et al. (2016). Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 monoclonal antibodies suppress acute simian-human immunodeficiency virus viremia and limit seeding of cell-associated viral reservoirs. J. Virol. 90, 1321–1332. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02454-15, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

