Immunoprotective test and whole-genome sequencing analysis of the attenuated S02 strain of Streptococcus iniae
- PMID: 40529591
- PMCID: PMC12170510
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1550544
Immunoprotective test and whole-genome sequencing analysis of the attenuated S02 strain of Streptococcus iniae
Abstract
Background: Streptococcus iniae is one of the most serious diseases threatening tilapia aquaculture, causing huge economic losses every year. Injectable attenuated vaccines are still the best choice for preventing streptococcal diseases affecting the tilapia.
Objective: This study evaluated the safety, stability, immunogenicity, antibody production time, and immune dose of the attenuated S02 strain of S. iniae and comprehensively analyzed the possible mechanisms of its attenuated virulence at the whole-genome level.
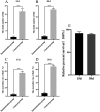
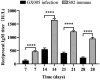
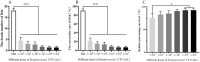
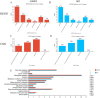
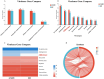
Results: After detoxification, the S02 strain completely loses its pathogenicity to tilapia and has good immunogenicity. The results of the backpropagation safety test showed that the S02 strain did not cause disease or death to tilapia after continuous passage for 50 generations. AfterS02 was injected, the immunoglobulin M (IgM) level in the serum was significantly higher than that in the GX005 infection group within 28 days and reached its peak at 14 days. An intraperitoneal injection of 109 CFUs/mL of S02 at a dose of 0.2 mL per fish had the best relative protection rate of 92.58%. The whole-genome sequencing results showed that the S02 strain had two large 0.2 Mbp segments of inversion compared to its parent virulence strain GX005, encoding 372 genes, including the virulence genes of the GNAT family N-acetyltransferase and the hyaluronic acid lyase genes of the hysA, hylA, and hylB, which are related to virulence factors.
Conclusion: This study provides theoretical data support for the prevention and control of the S. iniae infection in tilapia. The abnormal expression of important virulence genes GNAT family N-acetyltransferase and hyaluronic acid lyase genes hysA, hylA, and hylB caused by the inversion and translocation of large fragments could be the main mechanism for their attenuated virulence. This study provided theoretical support for the prevention and treatment of S. iniae infection in tilapia and the application of S02-attenuated vaccine.
Keywords: Streptococcus iniae; attenuated vaccine; immune protection; tilapia; whole genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2025 Yi, Lei, Liu, Tong, Huang, Quan, Chen and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
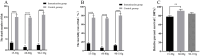
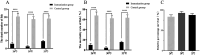

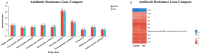
References
-
- Abdelkhalek N. K., Risha E., El-Adl M. A., Salama M. F., Dawood M. A. O. (2020). Antibacterial and antioxidant activity of clove oil against Streptococcus iniae infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and its effect on hepatic hepcidin expression. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 104, 478–488. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.05.064, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

