Genetic Subtype-Based International Prognostic Index Prognostic Model in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 40529616
- PMCID: PMC12171059
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70190
Genetic Subtype-Based International Prognostic Index Prognostic Model in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
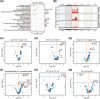
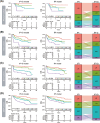
Molecular subtyping in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) leads to facilitating drug selection. However, an integrated prognostic model based on molecular subtyping and clinical features has not been well established. Here, we retrospectively performed whole genome sequencing, whole exome sequencing, and fluorescence in situ hybridization in newly diagnosed DLBCLs, established a simplified LymphType algorithm for classification evaluation, and proposed a new integrated prognostic stratification system, combined molecular subtypes and International Prognostic Index (IPI) scoring system in our in-house sequencing cohort (N = 100), and validated in three public cohorts (N = 1480). Compared with IPI scoring system and classification algorithm model alone, the discrimination ability of prognostic model based on the new integrated model showed best discrimination of overall survival with concordance index value (0.773 vs. 0.724 vs. 0.648). We subsequently established a four-category risk model defined for the integrated prognostic model as follows: low, low-intermediate, high-intermediate, and high risk, demonstrating stronger prognostic separation across all end points (all p < 0.001) in our in-house cohort and three validation cohorts. Collectively, the new feasible integrated prognostic stratification system contributes to accurate prognosis assessment in clinical routine and provides a new basis for the follow-up treatment.
Keywords: International Prognostic Index; LymphType; defined genetic subtype; diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma; integrated prognostic model.
© 2025 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Jiayue Qin, Lixia Liu, Shunli Yang, Libin Chen, Hong Chen, Feng Lou, and Shanbo Cao are the employees of Acornmed Biotechnology Co., Ltd., but has no potential relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Hilton L. K., Scott D. W., and Morin R. D., “Biological Heterogeneity in Diffuse Large B‐cell Lymphoma,” Seminars in Hematology 60, no. 5 (2023): 267–276. - PubMed
-
- Younes A., Brody J., Carpio C., et al., “Safety and Activity of ibrutinib in Combination With nivolumab in Patients With Relapsed non‐Hodgkin Lymphoma or Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia: A Phase 1/2a Study,” The Lancet Haematology 6, no. 2 (2019): e67–e78. - PubMed
-
- Xu P. P., Fu D., Li J. Y., et al., “Anthracycline Dose Optimisation in Patients With Diffuse Large B‐cell Lymphoma: A Multicentre, Phase 3, Randomised, Controlled Trial,” The Lancet Haematology 6, no. 6 (2019): e328–e337. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
