A Review on Pulsed Laser-Based Synthesis of Carbon and Graphene Quantum Dots in Liquids: From Fundamentals, Chemistry to Bio Applications and Beyond
- PMID: 40529787
- PMCID: PMC12172057
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5c01343
A Review on Pulsed Laser-Based Synthesis of Carbon and Graphene Quantum Dots in Liquids: From Fundamentals, Chemistry to Bio Applications and Beyond
Abstract
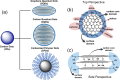
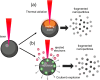
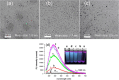
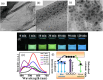
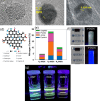
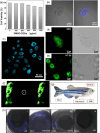
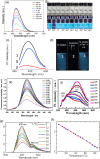
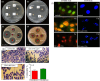
The constantly growing interest in zero-dimensional carbon-based nanomaterials such as carbon quantum dots (CQDs) and graphene quantum dots (GQDs) as the vital components in advancing various bio-related, catalysis, and energy-relevant applications has inspired nanotechnology research centered mainly on their synthesis and modifications for the betterment of their exceptional features including their strong and tunable fluorescence. Among the multitude of synthesis approaches in fabricating CQDs and GQDs, laser-based synthesis in liquids, such as pulsed laser ablation in liquids (PLAL) and pulsed laser fragmentation in liquids (PLFL), has emerged as a more beneficial technique owing to its versatility, flexibility, green synthesis process, and ease of scalability. With the modern trend of employing this method for CQDs and GQDs synthesis, this review article will revisit the foundation of laser synthesis in liquids, starting from its fundamental mechanism of nanoparticle formation to the effect of different variables such as laser parameters (e.g., laser energy, laser wavelength, frequency), chosen liquids, and the starting carbon material to the final attributes (morphological, optical, and surface) of CQDs and GQDs. In this paper, we will also address the different post-laser treatments, such as modifications and conjugation, and how they affect the properties of CQDs and GQDs. We will also emphasize the diverse applications of laser-synthesized CQDs and GQDs, ranging from bioapplications to beyond bio-related applications. This article hoped to provide practical insights for researchers to develop further laser synthesis in liquids to produce carbon-based nanomaterials such as CQDs and GQDs and their applicability to other applications.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures














References
-
- Alaghmandfard A., Sedighi O., Tabatabaei Rezaei N., Abedini A. A., Malek Khachatourian A., Toprak M. S., Seifalian A.. Recent Advances in the Modification of Carbon-Based Quantum Dots for Biomedical Applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2021;120:111756. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111756. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
