Patient journey and disease burden characterization of the population with phenylketonuria (PKU) in Brazil: a retrospective analysis through data reported in the public health system administrative database (DATASUS)
- PMID: 40529850
- PMCID: PMC12173015
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lana.2025.101134
Patient journey and disease burden characterization of the population with phenylketonuria (PKU) in Brazil: a retrospective analysis through data reported in the public health system administrative database (DATASUS)
Abstract
Background: In 2001, Brazil implemented a national newborn screening (NBS) for various conditions, including phenylketonuria (PKU). Data is lacking on the effectiveness of the NBS program in diagnosing PKU at birth and initiating treatment with a Phe-free amino acid-based formula within 30 days of diagnosis. This study evaluated the effectiveness of the NBS program and characterized the PKU population.
Methods: An observational, repeated cross-sectional population-based study was conducted using anonymized data from the Department of Informatics of the Unified Health System (DATASUS) in Brazil from 2008 to 2021. Only patients with confirmed diagnoses were included.
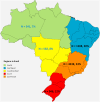
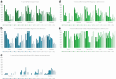
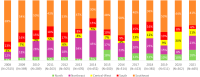
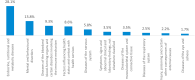
Findings: NBS coverage of live births within 30 days of birth was >80% for all years, while annual incidence of PKU ranged from 4 to 8 per 100,000 live births. Median time to screening diagnosis from birth was approximately 18 days (all years). DATASUS had 7615 patients with a record of PKU. The median age of the first record in DATASUS was 6.1 years, predominantly from the southeast region (53%). Also, 44% of the PKU population had a record of receiving Phe-free formula for treatment. Metabolic and related disorders were most prevalent in those <18 years of age (28.1%), while mental and behavioral disorders were most prevalent in those ≥18 years of age (100%).
Interpretation: Further investigations are necessary to enhance the effectiveness of NBS coverage, reduce the time from diagnosis to treatment initiation, improve Phe-free formula distribution, and improve DATASUS data quality.
Funding: The current study was funded by BioMarin Pharmaceutical, Novato, CA.
Keywords: Brazil; Newborn screening; Phenylketonuria; Public healthcare system; SUS.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
PRV: Has received honoraria as a speaker for BioMarin and travel support. Medical Advisor of Global Association of PKU (GAP) in Brazil. Medical writing services funded by BioMarin. MOP: Has received speaker fees from BioMarin for the event Education on Pegvaliase for Phenylketonuria: A New Horizon for Phenylketonuria (PKU), held in Brazil in May 2024. BM: The author declares no conflict of interests related to this publication. PV: Has received honoraria as a speaker for BioMarin. Medical writing services funded by BioMarin. DRFV: The author declares no conflict of interests related to this publication. DM: Medical writing services funded by BioMarin. Was an employee of BioMarin at the time of the study, and owns stocks or stock options. TSPCM: Medical writing services funded by BioMarin. Was an employee of BioMarin at the time of the study, and owns stocks or stock options. KL: Currently an employee of BioMarin, and owns stocks. AP The author declares no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surveillance for Violent Deaths - National Violent Death Reporting System, 50 States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico, 2022.MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025 Jun 12;74(5):1-42. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7405a1. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025. PMID: 40493548 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive integrated disease management program for phenylketonuria (IDMP-PKU) from Türkiye: rationale, design and patient characteristics.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 Aug 1;20(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03702-7. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 40751258 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging Cognitive and Speech Ecological Momentary Assessment in Individuals With Phenylketonuria: Development and Usability Study of Cognitive Fluctuations in a Rare Disease Population.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Jun 3;9:e63644. doi: 10.2196/63644. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 40072884 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and odds of anxiety and depression in cutaneous malignant melanoma: a proportional meta-analysis and regression.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):24-35. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae011. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38197404
-
Prenatal administration of progestogens for preventing spontaneous preterm birth in women with a multiple pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 20;2019(11):CD012024. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012024.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31745984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blau N., Van Spronsen F.J., Levy H.L. Phenylketonuria. Lancet. 2010:1417–1427. Elsevier B.V. - PubMed
-
- Vockley J., Andersson H.C., Antshel K.M., et al. Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency: diagnosis and management guideline. Genet Med. 2014;16:188–200. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell J.J., Trakadis Y.J., Scriver C.R. Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Genet Med. 2011;13:697–707. - PubMed
-
- Borrajo G.J.C. Newborn screening in Latin America at the beginning of the 21st century. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007;30:466–481. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

