Fibrinogen-to-Albumin Ratio as a Novel Predictor of Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients
- PMID: 40529893
- PMCID: PMC12170443
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S520602
Fibrinogen-to-Albumin Ratio as a Novel Predictor of Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
Objective: Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a life-threatening complication in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (MHD), yet reliable biomarkers for early risk stratification remain scarce. The fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio (FAR), a composite inflammatory and nutritional marker, may offer predictive value for ICH in this high-risk population.
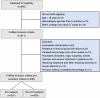
Methods: This retrospective study analyzed a total of 536 MHD patients (ICH group: n=207; non-ICH group: n=329) from June 2019 to June 2024. FAR was calculated based on laboratory parameters. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis was used to identify independent risk factors for ICH, and ROC curve analysis and restricted cubic spline (RCS) modeling were used to assess the predictive performance of FAR for cerebral hemorrhage in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Finally, the DeLong test was used to compare the differences in area under curve (AUC).
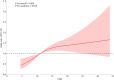
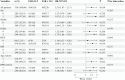
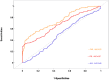
Results: Logistic regression analysis revealed that FAR ([OR] 1.07, 95% [CI] 1.03-1.10, p<0.001) was the independent predictor of ICH. Trend testing showed a dose-response correlation between FAR (p for trend <0.001) and ICH risk. RCS showed a non-linear correlation between FAR and ICH risk (non-linear p=0.029). ROC analysis demonstrated FAR's superior accuracy (AUC=0.75) compared to fibrinogen (AUC=0.67) and albumin (AUC=0.49), identifying 12.2 as the optimal cutoff (sensitivity=0.73, specificity=0.60). The DeLong's test confirm that FAR exhibits significantly superior discriminatory performance.
Conclusion: FAR may predict the occurrence of ICH in MHD patients. This study explores the application value of FAR in predicting ICH risk in MHD patients, providing a new biomarker for early identification of high-risk patients in clinical practice.
Keywords: albumin; fibrinogen; fibrinogen to albumin ratio; intracerebral hemorrhage; maintenance hemodialysis.
© 2025 He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Feigin VL, Roth GA, Naghavi M, et al. Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries and Risk Factors Study 2013 and Stroke Experts Writing Group. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(9):913–924. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30073-4. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

