Systemic Embolism From Aortic Arch Thrombus Following Warfarin Discontinuation: A Case Report
- PMID: 40530209
- PMCID: PMC12172004
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.84319
Systemic Embolism From Aortic Arch Thrombus Following Warfarin Discontinuation: A Case Report
Abstract
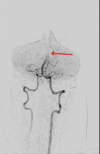
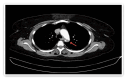
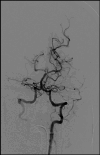
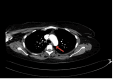
We present the case of a 40-year-old female with a previous diagnosis of unprovoked deep vein thrombosis (DVT), who had been on long-term warfarin therapy but discontinued it one month before presentation. She arrived at the emergency department following two episodes of transient loss of consciousness at work, raising concerns for a possible cerebrovascular event. Further evaluation revealed evidence of systemic embolization, as she developed acute basilar artery thrombosis and left upper limb ischemia findings consistent with multiple embolic events. Computed tomography angiography (CTA) demonstrated a mural thrombus in the thoracic aorta and occlusion of the left brachial artery. The patient received intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rTPA), followed by successful mechanical thrombectomy of the basilar artery. She was managed with systemic anticoagulation and discharged neurologically intact. This case highlights the critical importance of maintaining anticoagulation in high-risk individuals and demonstrates the potentially life-threatening consequences of abrupt discontinuation.
Keywords: anticoagulation discontinuation; basilar artery thrombosis; cerebral embolism; embolic stroke; enoxaparin; mechanical thrombectomy; mural thrombus; upper limb ischemia; warfarin cessation.
Copyright © 2025, Elrefaeei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Posterior circulation cerebrovascular syndromes: diagnosis and management. Schulz UG, Fischer U. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2017;88:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Clinical impact of bleeding in patients taking oral anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism: a meta-analysis. Linkins LA, Choi PT, Douketis JD. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:893–900. - PubMed
-
- Outcome in basilar artery occlusion treated with antithrombotic therapy or intra-arterial thrombolysis in the Basilar Artery International Cooperation Study (BASICS): a prospective registry study. Schonewille WJ, Algra A, Serena J, et al. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:724–730. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
