Refractory Diarrhea After Dor Fundoplication: The Long-Term Impact of Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy
- PMID: 40530222
- PMCID: PMC12170260
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.84301
Refractory Diarrhea After Dor Fundoplication: The Long-Term Impact of Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy
Abstract
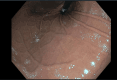
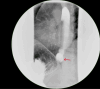
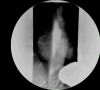
Persistent diarrhea following hiatal hernia repair is a rare but noteworthy postoperative complication. In this case, we present a 62-year-old female with a longstanding history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) responsive to proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). After undergoing robotic-assisted hiatal hernia repair with partial fundoplication, the patient discontinued PPI therapy and subsequently developed chronic diarrhea. Extensive testing, including stool cultures, returned negative, and antidiarrheal medications provided minimal relief. Interestingly, reintroduction of PPI therapy resulted in a complete resolution of symptoms within days. This case suggests a possible correlation between cessation of long-term PPI use and gastrointestinal dysfunction, with chronic diarrhea manifesting as a withdrawal-like effect. Further investigation into the role of PPI discontinuation on gut microbiota and its clinical outcomes is necessary to understand this phenomenon better.
Keywords: gerd; hiatal hernia; partial fundoplication; proton pump inhibitor; refractory diarrhea.
Copyright © 2025, Mangum et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. IRB, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Lubbock issued approval Exempt. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-reflux mucosectomy for proton pump inhibitor refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease with hiatal hernia: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Feb 21;104(8):e41166. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041166. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39993080 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical treatment strategies for gastroesophageal reflux after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 29;15:1463567. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1463567. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39534257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Baclofen as Add-on Therapy for Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Meta-analysis.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 1;59(6):512-523. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000002021. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 38869961 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Proton Pump Inhibitors and Emerging Acid-Suppressive Therapies in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2025 May 17;17(5):e84311. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84311. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40535413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation-induced injury and the gut microbiota: insights from a microbial perspective.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 16;18:17562848251347347. doi: 10.1177/17562848251347347. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40535532 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The appropriate use of proton-pump inhibitors. Savarino V, Marabotto E, Zentilin P, et al. Minerva Med. 2018;109:386–399. - PubMed
-
- Side effects of long-term proton pump inhibitor use: a review. Haastrup PF, Thompson W, Søndergaard J, Jarbøl DE. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018;123:114–121. - PubMed
-
- Long-term patient-reported outcomes after anti-reflux surgery for gastroesophageal reflux disease and hiatal hernia repair: a single-center experience. Peltrini R, Carannante F, Giovine G, et al. Minerva Surg. 2023;78:638–643. - PubMed
-
- Strategies for effective discontinuation of proton pump inhibitors. Kim J, Blackett JW, Jodorkovsky D. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2018;20:27. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources