Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of T2-Weighted Imaging Signal Variations in Prostate MRI Following Different Abstinence Periods: A Study in Young Healthy Men
- PMID: 40530245
- PMCID: PMC12170790
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S517266
Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of T2-Weighted Imaging Signal Variations in Prostate MRI Following Different Abstinence Periods: A Study in Young Healthy Men
Abstract
Objective: This study evaluates the impact of an abstinence period on the image quality of high-field prostate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
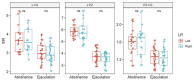
Methods: Male patients who underwent prostate MRI at Xi'an No.3 hospital between November 2021 and November 2022 were included in this study. The patients were divided into two groups based on whether they had ejaculated within three days prior to the MRI examination. Two radiologists assessed the boundary sharpness of the peripheral zone (PZ) and central gland (CG) using a double-blind 3-Point Likert scale. Regions of interest (ROIs) were marked bilaterally on the PZ and CG in sagittal T2-weighted images (T2WI). The signal intensity (SI) of the ROIs was measured, and the signal intensity ratio (SIR) was subsequently calculated. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test and independent samples t-test were employed to compare differences between the two groups.
Results: A total of 50 young male patients participated in the study, with 20 patients having an abstinence period of more than 3 days and 30 patients having an abstinence period of 3 days or less. Qualitative analysis revealed that the prostate structures were more easily identifiable in the abstinence group compared to the ejaculation group (P ≤ 0.05). Quantitative analysis showed that the SIR of the PZ and CG was lower in the ejaculation group than in the abstinence group (P ≤ 0.05 for both), with a particularly significant difference observed in the peripheral zone.
Conclusion: To obtain more accurate results in prostate MRI examinations, it is recommended that patients abstain from sexual activity for at least 3 days prior to the examination.
Keywords: MRI; T2-weighted imaging; image quality; prostate.
© 2025 Ma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High Risk of Venous Thromboembolism With Aspirin Prophylaxis After THA for High-riding Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Retrospective, Comparative Study.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jun 9. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003482. Online ahead of print. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40536765
-
Return to Running After Achilles Tendon Repair: How Do US Navy Service Members' Physical Readiness Tests Change After Undergoing an Achilles Tendon Repair?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jun 18. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003590. Online ahead of print. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40536551
-
Uncovering prostate cancer aggressiveness signal in T2-weighted MRI through a three-reference tissues normalization technique.NMR Biomed. 2024 Mar;37(3):e5069. doi: 10.1002/nbm.5069. Epub 2023 Nov 21. NMR Biomed. 2024. PMID: 37990759
-
Prenatal administration of progestogens for preventing spontaneous preterm birth in women with a multiple pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 20;2019(11):CD012024. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012024.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31745984 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and odds of anxiety and depression in cutaneous malignant melanoma: a proportional meta-analysis and regression.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):24-35. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae011. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38197404
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

