m6A methylation: a new frontier in epilepsy research and therapeutics
- PMID: 40530256
- PMCID: PMC12171009
- DOI: 10.17179/2025-8359
m6A methylation: a new frontier in epilepsy research and therapeutics
Abstract
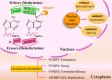
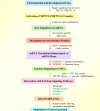
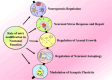
Epilepsy is a highly complex and global neurological disorder, for which available treatments only inadequately control the disease in many patients. Recent advances in molecular research have identified N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modifications as key regulators of neuronal processes that underpin the pathophysiology of epilepsy. This review critically discusses the emerging significance of m6A modifications in epilepsy, focusing on dynamic regulations of m6A "writers," "erasers," and "readers" for modulating gene expression, neuronal excitability, and synaptic plasticity in epilepsy. Dysregulation of m6A machinery promotes epilepsy by exacerbating oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuronal damage. We also discuss the prognostic significance of m6A alterations as a potential biomarker in epilepsy diagnosis and disease progression, along with advanced therapeutic strategies against m6A, including small molecules, RNA editing technologies, and precision medicine. This review highlights the transformational significance of m6A modulation in epilepsy therapy and opens new avenues for personalized therapeutic strategies that may revolutionize the field of drug-resistant epilepsy and improve the prognosis for patients. See also the graphical abstract(Fig. 1).
Keywords: epilepsy; m6A modification; m6A regulators; molecular biomarkers; neurodegeneration; precision medicine.
Copyright © 2025 Maqbool et al.
Figures
References
-
- Akichika S, Hirano S, Shichino Y, Suzuki T, Nishimasu H, Ishitani R, et al. Cap-specific terminal N (6)-methylation of RNA by an RNA polymerase II-associated methyltransferase. Science. 2019;363(6423) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
