Sorghum aphid/greenbug: current research and control strategies to accelerate the breeding of aphid-resistant sorghum
- PMID: 40530263
- PMCID: PMC12171870
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1588702
Sorghum aphid/greenbug: current research and control strategies to accelerate the breeding of aphid-resistant sorghum
Abstract
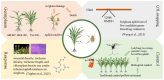
Sorghum, one of the world's five major cereal crops, faces significant yield losses due to aphid infestations, particularly from the sorghum aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) and the greenbug (Schizaphis graminum). These pests not only cause a reduction in grain yield, but also transmit plant viruses, posing a serious threat to global food security. Current strategies to mitigate aphid damage include large-scale insecticide applications, biological control through natural enemies, and the development of aphid-resistant sorghum varieties. However, the resistance genes of aphids and their mechanisms are still unclear, which poses a major challenge to breeding programs. This review synthesizes recent advances in understanding the interactions between sorghum and these two major aphid species, exploring topics such as aphid classification, quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping of resistance genes, and the molecular mechanisms of sorghum-aphid interactions. We also discuss conventional and emerging insecticide methods, biological control strategies, and their associated challenges. Looking ahead, the integration of molecular breeding techniques, including genetic engineering and genome editing, holds promise for accelerating the development of aphid-resistant sorghum varieties. These innovative approaches aim to minimize aphid damage, enhance sorghum productivity, and contribute to global food security in the face of climate change and evolving pest pressures.
Keywords: QTL mapping; aphid resistance mechanisms; chemical and biological control; food security; greenbug; molecular breeding; sorghum; sorghum aphid.
Copyright © 2025 Jiao, Wang, Ma, Shi, Wang, Guo and Lv.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of QTLs for aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) resistance in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) based on BSA-seq and analysis of candidate genes.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Aug 16;25(1):1081. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-07028-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40819068 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of combining aphid and headworm management on natural enemy conservation and grain sorghum production.J Econ Entomol. 2025 Aug 29;118(4):1721-1730. doi: 10.1093/jee/toaf108. J Econ Entomol. 2025. PMID: 40411369
-
Employing Spectral Features to Accelerate Sorghum Phenotyping Against Sap-Feeding Aphids.Plant Direct. 2025 Jul 8;9(7):e70092. doi: 10.1002/pld3.70092. eCollection 2025 Jul. Plant Direct. 2025. PMID: 40630052 Free PMC article.
-
Breeding for resistance to maize streak virus: challenges, progress and future directions: a review.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jun 3;16:1590870. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1590870. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40530294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Russian wheat aphid: a model for genomic plasticity and a challenge to breeders.Insect Sci. 2025 Aug 19. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.70144. Online ahead of print. Insect Sci. 2025. PMID: 40828227 Review.
References
-
- Al-Mousawi A. H., Richardson P. E., Burton R. L. (1983). Ultrastructural studies of greenbug (Hemiptera: aphididae) feeding damage to susceptible and resistant wheat cultivars. Ann. Entomological Soc. America 76, 964–971. doi: 10.1093/aesa/76.6.964 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

