Review of sensory systems deployed by epidermal keratinocytes
- PMID: 40530329
- PMCID: PMC12171141
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1598326
Review of sensory systems deployed by epidermal keratinocytes
Abstract
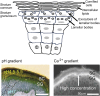
Recent studies have shown that epidermal sensory receptors intercept and direct responses to potentially threatening environmental factors, including shifts in temperature, electric potential, sound, acidity, light, taste, and odor. In addition to stimulating epidermal responses, activation of keratinocytes by these stressors can directly signal the central nervous system. Changes in epidermal permeability barrier homeostasis also depend upon ion dynamics, particularly alterations in intraepidermal gradients of calcium (Ca2+) and pH. The purpose of this review is to update readers about recent advances in the field of cutaneous sensory receptors, focusing upon their roles in mediating not only permeability barrier function, but also whole-body physiology and certain aspects of mental status.
Keywords: barrier homeostasis; central nervous system; epidermis; keratinocyte; pH; sensory receptor.
Copyright © 2025 Denda and Elias.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

